Third Year
THIRD YEAR – ENGLISH SEMESTER – I
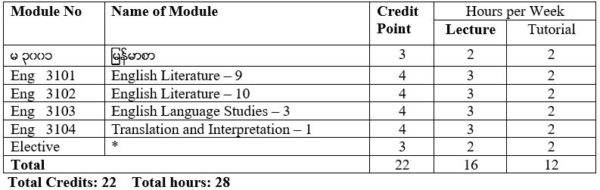
Foundation Course
မ ၃၀၀၁ ျမန္မာစာ
Core Courses
Eng 3101 English Literature – 9 (19thand 20th Century Short Stories and The Novel)
Eng 3102 English Literature – 10(18th and 19th Century Poetry and Drama)
Eng 3103 English Language Studies – 3 (Morphology)
Eng 3104 Translation & Interpretation – 1
Elective Courses (for English Specialistion)
Eng 3105 Communicative Skills – 5
Eng 3106 Business English – 1
Eng 3107 Introducing ELT Methodology – 1
Elective Courses (for Other Specialisations)
Eng 3003 Developing Communicative Skills– 3
* An English specialisation student will have to take one elective.
Eng 3101: English Literature – 9 (19th & 20th century Short Stories & The Novel)
Course Description
This module includes a selection of the 19th and 20th century English short stories and novels. Setting, plot, characterization, literary devices, climax, point of view, theme, symbols, conflicts, and development of the story are the focus of this module. This module will enhance the students’ ability to arrive at the correct interpretation of the writer’s message and to appreciate literature from different points of view.
The novels in the 19th and 20thcenturies particularly engaged the students in the events, circumstances, beliefs and attitudes in those periods. It concentrates on a critical study of works by the centuries’ major literary figures like Katherine Mansfield, Graham Greene, George Orwell, etc. The focus is on understanding the role of the novel in representing life and people and exploring socio-cultural changes, the flexibility of the genre and how it developed aesthetically, stylistically and structurally. This module also expands students’ literary vocabulary, and exercises critical reading and writing.
19th& 20th Century (Short Stories)
- Bliss (1918) Katherine Mansfield
- The Destructors Graham Greene
19th& 20th Century (The Novel)
- Animal Farm George Orwell
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the module, students will be able to:
- read and write critically and reflectively
- respond logically and creatively orally and in writing to what they read
- understand the literary aspects of the novel through written assignments
- develop critical thinking and creative thinking of the students.
Assessment
There are six assignments / presentations (individual and group work) that make up 20%, and the final closed book written examination of 80%. The assignments / presentations are based on the materials used in class.
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in the class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of four tutorials, which test the students’ understanding of what they have learnt
- completion of one written assignment and one group project
- completion of the final examination.
References for Short Stories
Dolley, C. (1967). The Penguin Book of English Short Stories. Great Britain: Penguin Books Ltd.
Konigsberg, I. (1971) The Classic Short Story. U.S.A.: Harper and Row Inc.
Mizener, A. (1967). Modern Short Stories: The Uses of Imagination. U.S.A.: Norton & Company, Inc.
Chin, B. A. et. al. (2002). Glencoe Literature: The Reader’s Choice. U.S.A.: The McGraw-Hill Companies.
Ridout, A. K. & Stuart, J. (1968). Short Stories for Discussion. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons.
References for The Novel
Alexander, Michael (2000) A History of English Literature. Macmillan. London
Drew, Elizabeth. (1967) The Novel: A Modern Guide to Fifteen English Masterpieces. Dell Publishing Co. Inc.
Lass, Abraham H. Ed. (1966) A Student’s Guide to 50 British Novels. Washington Square Press, Inc. New York.
Pickering, H. James, & Hoeper, D. Jeffrey. (1982) Literature. Macmillan Publishing Company. New York.
Eng-3102: English Literature 10 – (19th & 20th Century Poetry & Drama)
Course Description
This module deals with the study of poems and a play which are representative of 19th and 20th century poetry and drama. Studying selected English poems enables students to extend their knowledge of English poetry that they have already garnered in their academic pursuit. While pursuing the scholarly studies in English poetry, students simultaneously perceive the development of English poetry over the centuries. This module also engages students to learn a farcical comedy of Oscar Wilde, a famous Irish playwright. Through Wilde’s popular Victorian drama, students observe Wilde’s trademarks ‘satiric epigrams, paradoxes and puns’. It is Wilde’s popular work that represents the finest literature in the English language written during the 19th century and questions Victorian social values and norms. Moreover, how nineteenth-century intellectuals think through the relationship between dramatic form and the social world, and how nineteenth-century drama mobilizes new images of gender and the family can be learned through Wilde’s famous drama.
18th& 19th Century Poetry
- ‘Break, break, break’ Alfred Lord Tennyson
- The Tyger (from songs of experience) William Blake
- I wandered lonely as a cloud William Wordsworth (1804)
- Opening extract from ‘song of myself’ Walt Whitman
- Ozymandias Peter Bysshe Shelly
Drama
The Importance of Being Earnest Oscar Wilde
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students will be able to:
- recognize and explain the elements of poetry and drama through selected literary texts
- interpret critically certain ideas or messages that the authors of selected literary works are trying to illustrate
- evaluate the selected literary works and write reflections on them
Assessment
Class discussions during the lectures – 5%: Active engagement of students in class discussion is requested. Their active participation will be highly appreciated or graded.
Attendance – 5%: Students are to attend all lectures and their attendance will be one of the criteria in assessment.
Written Assignment – 5% of the grade is for written tasks assigned for the respective poems or acts in the play. Students are asked to work in groups so that they can learn from each other by sharing their own ideas in groups.
Presentation – 5%: 5% of the grade is allotted for students’ group presentation on the assigned tasks. In assessing group presentation, three-fold group assessment will be carried out. The teacher gives a grade to the group’s final product, group members give a grade to each other, and each group member gives a grade to him/herself, and justifies it. Every student’s grade is then a combination of: the teacher’s grade, average of peer grades, and self-assigned grades.
Exam – 80%: The grade is for students’ achievement in the final exam.
References for Poetry
Abrams, M. H. (1986) The Norton Anthology of English Literature. Vol. 1. USA: Norton and Company, Inc.
Hewett, R. P. (1984) A Choice of Poets: An Anthology of Poets from Wordsworth to the Present Day. UK: Nelson House.
Hoeper, Jeffrey D & James H. Pickering (1990) Poetry: An Introduction. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Kloeppel, L. A Teacher’s Guide to ‘The Importance of Being Earnest and Other Plays’. The Signet Classic Edition.
Pickering, James H. & Jeffrey D Hoeper (1986) Literature. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Wilkie, Brian & James Hurt (1998) Literature of the Western World. Vol. I. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
References for Drama
Abrams, M. H. (1986) The Norton Anthology of English Literature. Norton & Com. Inc
Alexander, M (2000) A History of English Literature. Macmillan Press Ltd.
Allison, Alexander W. et al. (1986) Masterpieces of Drama. Macmillan Publishing Co.
Pickering, James H. & Jeffrey D Hoeper (1986) Literature. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Eng 3103: English Language Studies – 3 (Morphology)
Course Description
This module acquaints learners of English with some background concepts of words and rules of word formation. Moreover, it also deals with morphemes: free and bound morphemes, lexical and functional morphemes, inflectional versus derivational morphology, and morphological analysis. The objective of this module is to provide an introduction to major concepts in the study of morphology and discusses its place within linguistic theory.
Morphology
- Words: Some background concepts
- Complex words and morphemes
- How are new words created?
- Inflectional versus derivational morphology
- Problematic aspects of morphological analysis
- Morphemes: The Minimal Units of Meaning
- (Bound and Free Morphemes, Prefixes and Suffixes, Infixes, Circumfixes, Roots and Stems, Huckles and Ceives)
- Rules of Word Formation
- (Derivational morphology, the hierarchical structure of words, more about derivational morphemes, lexical gaps)
- Sign Language Morphology
- Word Coinage (Compounds, Meaning of Compounds)
- Grammatical morphemes (Inflectional morphemes, exceptions and suppletions, morphology and syntax)
- Morphological analysis: Identifying morphemes
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the module, students will be able to:
- identify different types of morphology
- demonstrate how morphology is used across languages in a theoretically-informed way
- make informed judgements on the basis of cross-linguistic evidence to better understand the properties of their own native language
- discuss the relationship between morphology and other components of language, such as phonology, syntax and semantics
- engage in relevant research work.
Assessment
Assessment will be done through a combination of tutorial-based assessment: quizzes, group presentations, individual/group assignments (20%) and a final closed book examination (80%).
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in the class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of four tutorials, which test the students’ understanding of what they have learnt
- completion of one written assignment and one group project
- completion of the final examination.
References
Akmajan, A. et al. (2001). Linguistics: An Introduction to Language and Communication. Chapter 2
Fromkin, V. Rodman, R. & Hyams, N. (2003). An Introduction to Language. Heinle. Chapter 2
Thomas, W. Stewart, Jr. & Vaillette, N. (eds). Language Files. Columbus: The Ohio State University Press. File 5
Eng 3104: Translation and Interpretation – 1
Course Description
This module deals with the theoretical aspect of translation and translation studies, the background history of translation, general types of translation, features of a good translation, and directives by different translators. It trains students to apply their theoretical knowledge to the practice of translation. It also focuses on conceptual bases required to understand both the principles and recurrent issues, and difficulties in professional translation and interpreting.
- Introduction to Translation and Interpretation
- Translation: Definition and General Types
- Translation Equivalence
- Main Issues of Translation Studies
- The concepts of translation
- What is translation studies?
- A brief History of the Discipline
- The Holmes/ toury ‘map’
- Development since the 1970s
- Summary
- Discussion and Research Points
- Translation Theory Before the Twentieth Century
- Introduction
- ‘Word-for-word’ or ‘Sense-for-sense’
- Martin Luther
- Faithfulness, spirit and truth
- Early attempts at systematic translation theory: Dryden, Dolet and Tytler
- Schleiermacher and valorization of the foreign
- Translation theory of the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries in Britain
- Towards contemporary translation theory
- Summary
- Discussion and research points
- The Components of Translation Competence
- Types of Interpretation
- Translation and Interpretation Exercises
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the module, students will be able to:
- identify the differences between translation and interpretation and identify the different set skills required.
- analyze and evaluate translation works in terms of extent, level and rank based on the linguistic theory of translation
- apply the word-for-word, literal and free translation methods and choose the suitable one to translate a particular text
- define the two different types of interpretation and apply the voice shadowing and sight interpretation
Assessment
Assessment will be done through a combination of tutorial-based assessment, class and group discussions and formal written assignments and a final closed book written examination.
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in the class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of four tutorials, which test the students’ understanding of what they have learnt and their ability to apply the theoretical knowledge in their own translation and assessing others’ works
- completion of one written assignment and one group project
- completion of the final examination.
References
Baker, Mona (1992) In Other Words: A Course book on Translation. Routledge.
Carford. J.C (1965) A Linguistic Theory of Translation. OUP.
Gile, D. (2009) Basic Concepts and Models for Interpreters and Translator Training. John Benjamins Publishing Company. Denmark.
Munday, J (2001) Introducing Translation Studies Routledge.
Newmark, P (1988) A Textbook of Translation. Prentice Hall International (UK) Ltd.
Newmark, P (1993) Paragraphs on Translation. Longman.
Win Pe, U, et al., (2008) Translators’ Reference.Volume I. Shwe Pyi Taw Press
Eng 3105: Communicative Skills – 5
Course Description
This Module aims at developing students’ language proficiency, communicative skills and study skills. It introduces language items in authentic and semi-authentic engaging reading and listening texts. It also exposes students to different styles of written texts. Engaging activities will be given to make students practise the language structure, vocabulary and grammar rules in a variety of meaningful contexts to develop their reading, writing, speaking, pronunciation and writing skills with strong emphasis on the area of critical thinking skills. This module enables students to express their ideas and develop their communicative abilities through its engaging content and systematic skills work.
Learning Outcomes
After the course, students will be able to:
- apply grammar rules and vocabulary appropriate to their communication needs
- integrate study skills to improve their language and communication skills
- identify appropriate language styles for different social contexts
- produce different types of written texts systematically
- confidently use English in any social context
Assessment
Assessment will be done through a combination of tutorial-based assessment, class and group discussion, formal written assignments, presentations and a final examination.
Students will be able to demonstrate the completion of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in the class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of six tutorials based on reading, writing, listening, speaking, vocabulary, and grammar.
- completion of final closed book examination on all language skills
Prescribed Coursebook
Clandfield, L (2010) Global. Level 3 Course book, T’s book, Work book), Macmillan Publishing House.
References
Acklam, R.& Crace, A. (2008) Total English, Upper Intermediate, Students’ Book. London: Pearson Longman.
Clare, A.& Wilson, J. J. (2008) Total English, Upper Intermediate, Work Book. London: Pearson Longman.
Naughton, D. (2008) Total English, Upper Intermediate, Teacher’s Resource Book. London: Pearson Longman.
Harris, M. et al. (2006) New Opportunities, Pre-intermediate, Students’ Book. London: Longman.
Dean, M. et al. (2006) New Opportunities, Pre-intermediate, Teacher Book. London: Pearson Education Ltd.
Eng 3106 Business English – 1
Course Description
This module covers all the four language learning skills, grammar points and vocabulary that are used in business communication. It also focuses on different areas of business that closely reflect business undertakings. It aims to develop students’ spoken and written English, enabling them to use it accurately and appropriately. The course provides updated content and a significantly enhanced range of authentic resource material, reflecting the latest trends in the business world.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students will be able to
- develop their language skills as well as the content knowledge regarding respective business functions, and
- develop confidence to deal with people and business issues in the business world.
Assessment
Exam 80 marks + Tutorial 20 marks
There will be at least 5 tutorials for each semester. Group presentations, role plays, group or individual assignments will also be counted as tutorial.
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in the class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of four tutorials, which test the students’ understanding of what they have learnt
- completion of one written assignment and one group project
- completion of the final examination.
Prescribed Coursebook
Market Leader (Intermediate Business English Course Book, 3rd Edition), David Cotton, David Falvey & Simon Kent, Pearson Longman Press
References
Mascull, Bill (2002) Business Vocabulary in Use. CUP.
Naunton, Jon (2005) Profile 1Pre-intermediate, Oxford Business English. OUP.
Eng 3107: Introducing ELT Methodology – 1
Course description
This module introduces the theoretical background to the practice of English language teaching. It also aims to develop students’ awareness of learner differences and its importance in language teaching, different roles of teacher and different teaching methods that are helpful in the realization of teaching methodology.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the module, students will be able to:
1) classify learners according to their age;
2) analyse learners based on learner differences such as aptitude, learning styles, language levels, motivation, etc.;
3) identify teacher’s roles in language teaching;
4) determine the appropriate teaching methods.
Assessment
Assessment will be done through the following modes:
- a formal written examination (80%)
- a combination of tutorial-based assessment, class and group discussion and formal written assignments (20%)
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in class and group discussions
- completion of tutorials, which test the students’ understanding of theories
- completion of micro teaching
- completion of formal written examination
References
Harmer, J (1998) The Practice of English Language Teaching. Longman group Ltd. Pg 37 -197.
Edwards, C & Willis, J. (2005) Teachers Exploring Tasks in English Language Teaching. New York: Palgrave Macmillan
THIRD YEAR – ENGLISH SEMESTER – II
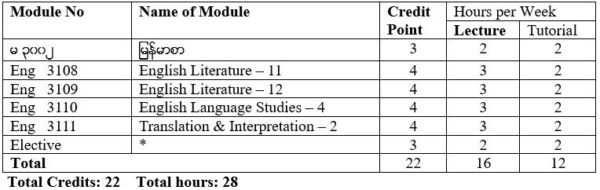
Foundation Course
မ ၃၀၀၁၂ ျမန္မာစာ
Core Courses
Eng 3108 English Literature – 11 (19th and 20th Century Short Stories and The Novel)
Eng 3109 English Literature – 12 (18th and 19th Century Poetry and Drama)
Eng 3110 English Language Studies – 4 (Syntactic Theory – 1)
Eng 3111 Translation & Interpretation – 2
Elective Courses (for English Specialisation)
Eng 3112 Communicative Skills – 6
Eng 3113 Business English – 2
Eng 3114 Introducing ELT Methodology – 2
Elective Courses (for Other Specialisations)
Eng 3004 Developing Communicative Skills – 4
* An English specialisation student will have to take one elective.
Eng 3108: English Literature – 11 (19th & 20th century Short Stories & The Novel)
Course Description
This module includes a selection of the 19th and 20th century English short stories and a novel. Short stories are studied with particular attention to setting, plot, characterization, literary devices, climax, point of view, theme, symbols, conflicts, and development of the story. This module will enhance the students’ ability to arrive at the correct interpretation of the writer’s message and to appreciate literature from different points of view.
This module deals with the novel in the 19th and 20thcenturies which were particularly engaged with the events, circumstances, beliefs and attitudes of their time. It concentrates on a critical study of works by the centuries’ major literary figures like RK Narayan, H.G.Wells, Harper Lee,
etc. The focus is on the role of the novel in representing life and people, and exploring social and cultural changes, the flexibility of the genre and how it developed aesthetically, stylistically and structurally. This module also expands literary vocabulary, and exercises critical reading and writing skills.
19th& 20th Century (Short Stories)
- A Horse and Two Goats RK Narayan
- The Door in the Wall H.G.Wells
19th& 20th Century (The Novel)
To Kill a Mockingbird Harper Lee
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the module, students will be able to:
- read and write literary works critically and reflectively
- respond to what they read logically and creatively in writing
- analyse the literary aspects of the novel through written assignments
Assessment
There are six assignments / presentations (individual and group work) that make up 20% and the other 80% goes to the completion of the final closed book written examination of this course. The assignments / presentations are related to the material covered in class.
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in the class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of four tutorials, which test the students’ understanding of what they have learnt
- completion of one written assignment and one group project
- completion of the final examination.
References for Short Stories
Dolley, C. (1967). The Penguin Book of English Short Stories. Great Britain: Penguin Books Ltd.
Konigsberg, I. (1971) The Classic Short Story. U.S.A.: Harper and Row Inc.
Mizener, A. (1967). Modern Short Stories: The Uses of Imagination. U.S.A.: Norton & Company, Inc.
Chin, B. A. et. al. (2002). Glencoe Literature: The Reader’s Choice. U.S.A.: The McGraw-Hill Companies.
Ridout, A. K. & Stuart, J. (1968). Short Stories for Discussion. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons.
References for The Novel
Alexander, Michael (2000) A History of English Literature. Macmillan. London
Drew, Elizabeth. (1967) The Novel: A Modern Guide to Fifteen English Masterpieces. Dell Publishing Co. Inc.
Lass, Abraham H. Ed. (1966) A Student’s Guide to 50 British Novels. Washington Square Press, Inc. New York.
Pickering, H. James, & Hoeper, D. Jeffrey. (1982) Literature. Macmillan Publishing Company. New York.
Eng-3109: English Literature – 12 (19th & 20th Century Poetry & Drama)
Course Description
This module deals with the study of poems and a play which are representative of 19th and 20th century poetry and drama. Studying selected 19th century English poems enables students to extend their knowledge of English poetry that they have already garnered in their academic pursuit. While pursuing the scholarly studies in English poetry, students simultaneously perceive the development of English poetry over the centuries. This module also engages students to learn a 20th century modern American tragedy of Arthur Miller, a famous American playwright. Through Miller’s play, students study what he is trying to say about ‘the American Dream’ of his time.
18th& 19th Century Poetry
- Porphyria’s Lover Robert Browning
- Ode to a Nightingale John Keats
- Pied Beauty Gerald Manley Hopkins
- A certain slant of Light Emily Dickinson
- She Walks in Beauty Lord Byron
Drama
Death of A Salesman Arthur Miller
Learning outcomes
At the end of the course, students will be able to:
- recognize and explain the elements of poetry and drama through selected literary texts
- critically interpret ideas or messages that the authors of selected literary works are trying to communicate with the readers
- evaluate the selected literary works and write reflections on them
Assessment
Class discussions during the lectures – 5%: Active engagement of students in class discussion is requested. Their active participation will be highly appreciated or graded.
Attendance – 5%: Students are to attend all lectures and their attendance will be one of the criteria in assessment.
Written Assignment – 5% of the grade is for written tasks assigned for the respective poems or acts in the play. Students are asked to work in groups so that they can learn from each other by sharing their own ideas in groups.
Presentation – 5%: 5% of the grade is allotted for students’ group presentation on the assigned tasks. In assessing group presentation, three-fold group assessment will be carried out. The teacher gives a grade to the group’s final product, group members give a grade to each other, and each group member gives a grade to him/herself, and justifies it. Every student’s grade is then a combination of: the teacher’s grade, average of peer grades, and self-assigned grades.
Exam – 80%: The grade is for students’ achievement in the final exam.
References for Poetry
Abrams, M. H. (1986) The Norton Anthology of English Literature. Vol. 1. USA: Norton and Company, Inc.
Hewett, R. P. (1984) A Choice of Poets: An Anthology of Poets from Wordsworth to the present day. UK: Nelson House.
Hoeper, Jeffrey D & James H. Pickering (1990) Poetry: An Introduction. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Pickering, James H. & Jeffrey D Hoeper (1986) Literature. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Tetu, R. A Teacher’s Guide to the Arthur Miller’s ‘Death of a Salesman’. The Penguin Edition.
Ward, Thomas Humphry (1883) The English Poets. Vol. IV. London: Macmillan and Co.
Weekes, A. R (year not mentioned) The Odes of John Keats. London: University Tutorial Press Ltd.
Wilkie, Brian & James Hurt (1998) Literature of the Western World. Vol. I. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
References for Drama
Abrams, M. H. (1986) The Norton Anthology of English Literature. Norton & Com. Inc
Alexander, Michael (2000) A History of English Literature. Macmillan Press Ltd.
Allison, Alexander W. et al. (1986) Masterpieces of Drama. Macmillan Publishing Co.
Pickering, James H. & Jeffrey, D Hoeper (1986) Literature. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Eng 3103: English Language Studies – 4 (Syntactic Theory – 1)
Course Description
This module concerns preliminaries to syntactic structure such as the goals of syntactic theory, the importance of syntactic theory, introduction to constituent structure, ways of representing constituent structure, investigation of constituent structure and phrasal categories. It also deals with types of syntactic rules, the relation between rules and sentences. Moreover, it also looks at the subcategorization through different approaches such as the Aspects approach, Principles and Parameters (P&P) approach and Phrase Structure Grammar (PSG) approach.
Syntactic Theory – 1
- Preliminaries (The goals of syntactic theory, acceptability and grammaticality, syntactic theory and traditional grammar, the importance of syntactic theory)
- Constituent structure (The motivation for constituent structure, the representation of constituent structure, the investigation of constituent structure, intermediate categories, some further categories)
- Syntactic rules (Phrase structure rules, rules and sentences, immediate dominants and linear precedence rules, non-local conditions on trees)
- Syntactic categories (Additional information about expressions, phrasal categories and word level categories, cross-categorical generalizations, features, categories in rules and the lexicon and categories in trees)
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the module, students will be able to:
- understand the basic terminology and concepts of syntactic description and theory
- identify syntactic categories and their features
- determine syntactic structure by constituency tests, representing the information in syntactic tree diagrams and labelled bracketing
- apply logical reasoning and problem-solving techniques in order to analyze new data
Assessment
Assessment will be done through a combination of tutorial-based assessment: quizzes, group presentations, individual/group assignments (20%) and a final closed book examination (80%).
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in the class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of four tutorials, which test the students’ understanding of what they have learnt
- completion of one written assignment and one group project
- completion of the final examination.
References
Akmajan, A. et al. (2001). Linguistics: An Introduction to Language and Communication. Chapter 5
Borsley, R. (1999). Syntactic Theory: A Unified Approach. London: Aronold. Chapter 1- 4 (Pg 1- 64)
Fromkin, V. & Rodman, R. (1993). An Introduction to Language. Chapter 3
Thomas, W. Stewart, Jr. & Vaillette, N. (eds). Language Files. Columbus: The Ohio State University Press. File 6
Eng 3111: Translation and Interpretation – 2
Course Description
This module deals with the theoretical aspect of the process of translating and translation procedures. Students will be able to put their theoretical knowledge into practice through the translation of lexis, proper names, idioms and proverbs, abbreviations and acronyms, first at the sentence level, and then at the paragraph level. It also focuses on basic theoretical components in interpreter and translator training, similarities and differences between interpreting and translation.
- Introduction to Translation and Interpretation
- Translation: Definition and General Types
- Translation Equivalence
- Main Issues of Translation Studies
The concepts of translation
What is translation studies?
A brief History of the Discipline
The Holmes/ Toury ‘map’
Development since the 1970s
Summary
Discussion and Research Points
- Translation Theory Before the Twentieth Century
Introduction
‘Word-for-word’ or ‘Sense-for-sense’
Martin Luther
Faithfulness, spirit and truth
Early attempts at systematic translation theory: Dryden, Dolet and Tytler
Schleiermacher and valorization of the foreign
Translation theory of the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries in Britain
Towards contemporary translation theory
Summary
Discussion and research points
- The Components of Translation Competence
- Types of Interpretation
- Translation and Interpretation Exercises
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the module, students will be able to:
- demonstrate the understanding of the concept of translation and translation studies
- compare and contrast the different assessment criteria and relate them to the practices
- apply various translation techniques in translation
- apply the summarizing and note taking techniques in interpretation
Assessment
Assessment will be done through a combination of tutorial-based assessment, class and group discussion and formal written assignments (20%) and a final examination (80%).
Students will be able to demonstrate the completion of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in the class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of four tutorials which assess the students’ understanding of what they have learnt and their ability to apply the theoretical knowledge in their own translation and assessing others’ works
- completion of two case studies
- completion of the final examination.
References
Baker, Mona (1992) In Other Words: A Course book on Translation. Routledge.
Carford. J.C (1965) A Linguistic Theory of Translation. OUP.
Gile, D. (2009) Basic Concepts and Models for Interpreters and Translator Training. John Benjamins Publishing Company. Denmark.
Munday, J (2001) Introducing Translation Studies Routledge.
Newmark, P (1988) A Textbook of Translation. Prentice Hall International (UK) Ltd.
Newmark, P (1993) Paragraphs on Translation. Longman.
Win Pe, U, et al., (2008) Translators’ Reference.Volume I. Shwe Pyi Taw Press
Eng 3112: Communicative Skills – 6
Course Description
This Module aims at developing students’ language skills, communicative skills and study skills. It introduces language items in authentic and semi-authentic engaging reading and listening texts. It also exposes students to different styles of written texts. Engaging activities will be given to make students practise the language structure, vocabulary and grammar rules in a variety of meaningful contexts to develop their reading, writing, speaking, pronunciation and writing skills with strong emphasis on the area of critical thinking skills. So, this module enables students to express their ideas and develop their communicative abilities through its engaging content and systematic skills work.
Learning Outcomes
After the course, students will be able to:
- apply grammar rules and vocabulary appropriate to their communication needs
- integrate study skills to improve their language and communication skills
- identify appropriate language styles for different social contexts
- produce different types of written texts systematically
- confidently use English in any social context
Assessment
Assessment will be done through a combination of tutorial-based assessment, class and group discussion, formal written assignments, presentations (20%) and a final examination (80%).
Students will be able to demonstrate the completion of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in the class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of six tutorials based on reading, writing, listening, speaking, vocabulary, and grammar.
- completion of closed book examination on all language skills
Prescribed Coursebook
Clandfield, L (2010) Global. Level 3 Course book, T’s book, Work book, Macmillan Publishing House.
References
Acklam, R.& Crace, A. (2008) Total English, Upper Intermediate, Students’ Book.London: Pearson Longman.
Clare,A.& Wilson,J. J. (2008) Total English, Upper Intermediate, Work Book.London: Pearson Longman.
Naughton,D. (2008) Total English, Upper Intermediate, Teacher’s Resource Book.London: Pearson Longman.
Harris, M. et al. (2006) New Opportunities, Pre-intermediate, Students’ Book.London: Longman.
Dean, M. et al. (2006) New Opportunities,Pre-intermediate, Teacher Book.London: Pearson Education Ltd.
Eng 3113 Business English – 2
Course Description
This module covers all the four language learning skills, grammar and vocabulary that are used in business communication. It also focuses on different areas of business that closely reflect business undertakings. It aims to develop students’ spoken and written English, enabling them to use it accurately and appropriately. The course provides updated content and a significantly enhanced range of authentic resource material, reflecting the latest trends in the business world.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students will be able to
- develop their language skills as well as the content knowledge regarding respective business functions, and
- develop confidence in deal with people and business issues in the business world.
Assessment
Exam 80 marks + Tutorial 20 marks
There will be at least 5 tutorials for each semester. Group presentations, role plays, group or individual assignments will also be counted as tutorial.
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in the class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of four tutorials, which test the students’ understanding of what they have learnt
- completion of one written assignment and one group project
- completion of the final examination.
Prescribed Coursebook
Market Leader (Intermediate Business English Course Book, 3rd Edition), David Cotton, David Falvey & Simon Kent, Pearson Longman Press
References
Mascull, Bill (2002) Business Vocabulary in Use. CUP.
Naunton, Jon (2005) Profile 1Pre-intermediate, Oxford Business English. OUP.
Eng 3114 (Introducing ELT Methodology – 2)
Course Description
This module deals with studying and researching language to increase knowledge of the English language system. It also focuses on teaching pronunciation techniques and the assessment of students’ performance and giving feedback. It explores various aspects of task-based teaching and learning and gives insights into ways in which tasks can be designed, adapted and implemented in a range of teaching contexts and illustrates ways in which tasks and task-based learning can be investigated as a research activity.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the module, students will be able to:
- apply knowledge and skills on their classroom technique
- discuss methodology for teaching all the skill sectors in ELT
- demonstrate a variety of ways in which teachers use tasks to better understand their teaching and their students’ learning
- continue their professional development alone or with others
Assessment
This module will be assessed through a combination of tutorial-based assessment: quizzes, group presentations, individual/group assignments (20%) and a final closed book examination (80%).
References
Harmer, J. (1998) The Practice of English Language Teaching Longman group Ltd. Pg 37-197.
Edwards, C. & Willis, J. (2005) Teachers Exploring Tasks in English Language Teaching. New York: Palgrave Macmillan

