Second Year
SECOND YEAR – ENGLISH SEMESTER –I
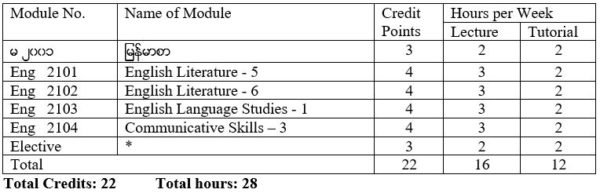
Foundation Course
မ ၂၀၀၁ ျမန္မာစာ
Core Courses
Eng 2101 English Literature – 5 (16th to 20th Century Prose and 19th and 20th Century Short Stories)
Eng 2102 English Literature – 6 (19th and 20th Century Poetry and Drama)
Eng 2103 English Language Studies – 1 (Introduction to General Linguistics and Phonetics)
Eng 2104 Communicative Skills – 3
Elective Courses (for English Specialisation)
Hist 2003 Social History of England
Psy 2001 Language and Thought
Phil 2001 History of Western Intellectual Development – 1
IR 2001 Elements of Political Institutions – 1
OS 2001 Pali Language
OS 2003 Pali Literature (Prose)
Elective Courses (for Other Specialisations)
Eng 2003 Developing Communicative Skills – 1
* An English specialisation student will have to take one elective
Eng 2101: English Literature – 5 (16th to 20th Century Prose and 19th& 20th Century Short Stories)
Course Description
This module introduces students to literature through a selection of 16th to 20th century prose passages and 19th& 20th century short stories by well-known writers in these periods. The selection is done from a variety of themes. This module helps students to extend their knowledge of styles of various types of prose passages and characteristics of short stories.
This module focuses more on characterization and tone of the text in particular. As short stories are mirrors of a certain age, the selection helps the students to gain knowledge about the author’s life, and the historical, social and cultural background of the story. This module trains students to read literary texts intensively, express their understanding of these texts both in class discussion and in writing, and develop language skills through literature.
16th& 20th Century Prose
Close reading (Prose)
- Chapter 15 – Characterization
15.1. Character types and roles
15.2. Character analysis
- Chapter 16 – The tone of the text: Comic, Tragic or Ironic
16.1. Comedy
16.2. Tragedy
16.3. Irony
19th& 20th Century Short Stories
- A Clean Well-Lighted Place Earnest Hemingway
- The Jockey Carson McCullers
- The Purloined Letter Edgar Allan Poe
- The Voyage Katherine Mansfield
- The Pomegranate Trees William Saroyan
Learning Outcomes
After this module, students will be able to:
- identify and analyze characterization techniques used by the different writers
- analyse a character in a short story
- identify and analyze the comic, tragic and ironic elements in a story
- create stories with different tones and characters using different characterization techniques
Assessment Criteria
Assessment will be done through a combination of tutorial-based assessment, class and group discussion and formal written assignments and a final closed book written examination.
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of four tutorials, which test the students’ understanding of what they have learnt
- completion of one written assignment/ project and one group presentation, and
- completion of the final closed book written examination
Prescribed Coursebook
Choo, S & Yeo, R (2013). Mining for Meaning. Learners Publishing Private Limited.
References for Prose
Abrams, M. H. (1986). The Norton Anthology of English Literature. (Fifth edition). New York: Norton & Company.
Armour, J. S. (1958). Standard English Essays. Bombay: Blackie and Son Ltd.
Boas, G. (1954). Modern English Prose. London: Macmillan & Co. Ltd.
Conlin, M.L. (1990). Patterns Plus: A Short Prose Reader with Argumentation. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company.
D’oyley, E. (1934). Modern Prose. London: Edward Arnold & Co.
Ridout, A. K. & Stuart, J. (1968). Short Stories for Discussion. New York: Charles Scribner’s.
Stafford, W. & Candelaria, F. (1966). The Voices of Prose. USA: McGraw. Hill, Inc.
References for Short Stories
Dolley, C. (1967). The Penguin Book of English Short Stories. Great Britain: Penguin Books Ltd.
Konigsberg, I. (1971) The Classic Short Story. U.S.A.: Harper and Row Inc.
Mizener, A. (1967). Modern Short Stories: The Uses of Imagination. U.S.A.: Norton & Company, Inc.
Chin, B. A. et. al. (2002). Glencoe Literature: The Reader’s Choice. U.S.A.: The McGraw-Hill Companies.
Ridout, A. K. & Stuart, J. (1968). Short Stories for Discussion. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons.
Eng 2102: English Literature – 6 (19th& 20th Century Poetry & Drama)
Course Description
This module deals with the study of a rich variety of poems, both British and American, which are representative of the period. The poems are selected and presented using a thematic approach. Students will be able to appreciate the selected poems expressed in English so that their language power in speaking and writing will be enhanced.
This module also deals with selections from English Drama of 19th and 20th centuries. Students will be able to read not only for pleasure but also to tackle conventional themes in the light of a new understanding of the theory and development of tragedy, comedy, and other modes of dramatic expression. It aims at helping students to develop their language through an intensive study of the style of writing in these plays, which introduce the on-setting element of modernism.
19th& 20th Century Poetry
- The World is Too much with us William Wordsworth
- The Road not Taken Robert Frost
- Invictus William Ernest Henley
- A Red, Red, Rose Robert Burns
- When I was One and Twenty A. E. Housman
- How Do I Love Thee Elizabeth Barrett Browning
19th& 20th Century Drama
- The Princess and the Swineherd Nicholas Stuart Gray
Learning Outcomes
After completing the course, students will be able to:
- gain knowledge of the culture-specific conventions of both British and American literatures
- appreciate the selected poems expressed in modern English so that their speaking and writing skills will be enhanced
- analyze the functions of texts and their relations with historical, social and political contexts, and
- analyze how purpose, style and genre function in texts to achieve particular literary, rhetorical and aesthetic effects.
Assessment
Assessment will be done through a combination of tutorial-based assessment (20%), and a final closed book written examination (80%).
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- completion of tutorial-based assessment; group works, written assignments, poster competition/ role play and the presentations
- completion of final closed book examination
References for Poetry
Abrams, M. H. (1986) The Norton Anthology of English Literature. Vol. 1. USA: Norton and Company, Inc.
Hewett, R. P. (1984) A Choice of Poets: An Anthology of Poets from Wordsworth to the present day. UK: Nelson House.
Hoeper, Jeffrey D & James H. Pickering (1990) Poetry: An Introduction. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Peacock, W (1963) English Verse. Vol. V. Oxford: OUP
Pickering, James H. & Jeffrey D Hoeper (1986) Literature. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Ward, Thomas Humphry (1883) The English Poets. Vol. IV. London: Macmillan and Co.
Weekes, A. R (year not mentioned) The Odes of John Keats. London: University Tutorial Press Ltd.
Wilkie, Brian & James Hurt (1998) Literature of the Western World. Vol. I. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Wollman, Maurice (1948) Poems of Twenty Years: An Anthology. London: Macmillan and Co.
References for Drama
Abrams, M. H. (1986) The Norton Anthology of English Literature. Norton & Com. Inc
Alexander, Michael (2000) A History of English Literature. Macmillan Press Ltd.
Allison, Alexander W. et al. (1986) Masterpieces of Drama. Macmillan Publishing Co.
Pickering, James H. & Jeffrey D Hoeper (1986) Literature. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Eng 2103: English Language Studies – 1 (Introduction to General Linguistics and Phonetics)
Course Description
This module introduces general linguistics and phonetics. The first part consists of the definition of language, the origin and development of human languages, characteristics and varieties of language, as well as animal and human language. It also focuses on the definition, the scope of linguistics, types of linguistics and its related fields. The second part deals with the definition of phonetics, its branches, and the description of vowels and consonants.
Contents
Part A:
Language
- Definition
- Origin and development of human language
- Characteristics
- Varieties
Linguistics
- Animal communication and human language
- The origin and development of human language
- Varieties of language
- Speech and writing
- What is language?
- What is linguistics?
- Is linguistics a science?
- The scope of linguistics
- Linguistic levels
- Linguistics and related fields
- Types of linguistics or linguistics and other branches of knowledge
- Descriptive, historical and comparative linguistics
Part B:
Phonetics
- Definition of phonetics
- History of phonetics
- Branches of phonetics
- The production of speech: the speech mechanism
- The description of speech
- Vowels
- Consonants
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the module, students will be able to
- discuss the history and characteristics of human language and animal communication
- use linguistic and phonetic knowledge in language learning
- distinguish speech sounds in English: for example, British English and American English, and
- transform words into phonemic scripts and vise visa.
Assessment
Assessment will be done through a combination of tutorial-based assessment, class and group discussion, formal written assignments (20%) and a final examination (80%).
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in the class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of three tutorials, which test the students’ understanding of what they have learnt
- completion of two written assignments, and
- completion of the final closed book written examination
References
Introduction to General Linguistics and Phonetics
Verma, S.K. & Krishnaswamy, N. (1989). Modern Linguistics: An Introduction. Dehli: OUP.
Radhey L.Varshney (2003). An Introductory Textbook of Linguistics and Phonetics. Bareilly: Student Store. Chapter 2 & 4
Kelly, G. (2000)How to teach pronunciation. England: Pearson Education Ltd.Chapter 1, 3, 4
Fromkin, V. Rodman, R. & Hyams, N. (2003). An Introduction to Language. Heinle. Chapter 6
Clark, J. & Yallop. C (1997). An Introduction and Phonetics and Phonology. UK: Blackwell Publishers Ltd. Chapter 2.
Eng- 2104: Communicative Skills -3
Course description
This module aims to develop students’ communicative skills and language skills: grammar, vocabulary, reading, listening, speaking, pronunciation, critical thinking skills, problem solving skills and creativity. Authentic or semi-authentic reading and listening texts taken from a variety of text types will be used to develop their reading and listening skills. In grammar section, students are encouraged to analyse and understand grammar through an inductive approach regarding examples in reading and listening texts and the vocabulary component pays attention to word building and lexical patterns and they are recycled through the speaking activities. The speaking section includes a variety of activities, which enable the students to comment on the topics and discuss the issues that arise, as well as talk about more personal experiences and knowledge and the writing section will develop students’ writing through analysis of models and practice in producing different text styles.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the module, students will be able to:
- utilize the language phrases for giving presentations, describing and evaluating qualities in a real-life situation
- produce a cause-effect essay, an online review, and a short formal report in a systematic way
- apply reading strategies: skimming, scanning, and proofreading
- use grammar patterns learned in real contexts
- develop their critical thinking skills, problem solving skills and creativity
Assessment
Assessment will be done through a combination of tutorial-based assessment, class and group discussion, formal written assignments, presentations (20%) and a final examination (80%).
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in the class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of six tutorials based on reading, writing, listening, speaking, vocabulary, and grammar.
- completion of individual written assignments and group presentation on a Mega Project
- completion of the final closed book written examination
Prescribed Coursebook
Cotton, D., Falvey, D. & Kent, S. (2014). New Language Leader 2: Coursebook. England: Pearson Education Limited.
References
https://english-dashboard.pearson.com
SECOND YEAR – ENGLISH SEMESTER –II

Foundation Course
မ ၂၀၀၂ ျမန္မာစာ
Core Courses
Eng 2105 English Literature – 7 (16th to 20th Century Prose and 19th and 20th Century Short Stories)
Eng 2106 English Literature – 8 (19thand 20th Century Poetry and Drama)
Eng 2107 English Language Studies – 2 (Introduction to English Phonology)
Eng 2108 Communicative Skills – 4
Elective Courses (for English Specialisation)
Hist 2006 Social History of England
Psy 2004 Stress and Stress Management
Phil 2006 History of Western Intellectual Development – 2
IR 2004 Elements of Political Institutions – 2
OS 2006 Pali Language
OS 2008 Pali Literature (Poetry)
Elective Courses (for Other Specialisations)
Eng 2004 Developing Communicative Skills – 2
* An English specialisation student will have to take one elective.
Eng 2105: English Literature – 7 (16th to 20th Century Prose & 19th& 20th Century Short Stories)
This module extends students’ knowledge of literature through a selection of 16th to 20th century prose passages and 19th& 20th century short stories by well-known writers in these centuries. Literary works with various themes were selected. This module helps students to study the style of various types of prose passages and the characteristics of short stories.
This module focuses more on prose genres and on the works of the great essayists. As short stories are mirrors of the age, the selection helps the students to gain knowledge about the author’s life, and the historical, social and cultural background of the story. This module trains students to read literary texts intensively and express their understanding of the selected texts both in class discussion and in writing.
16th to 20th Century Prose
- How to put off doing a job Andy Rooney
- August Andrei Codrescu
- Of studies Francis Bacon
- From the diary(the great fire) Pepys
- On familiar style Hazlitt
19th& 20th Century Short Stories
- Before the End of Summer Grant Moss Jr.
- Learn to Say Good-by Jessamyn West
- Odor of Chrysanthemums H. Lawrence
- The Lady or the Tiger? Frank R. Stockton
Learning Outcomes
After this module, students will be able to:
- compare and contrast essays and other forms of prose passages
- create prose passages on familiar topics and recreating the simplicity and style of the model prose passages
- detect underlying and foreshadowing techniques used in narration
- compare and contrast the stories based on their plot structure and other elements of narration and characterization
Assessment
Assessment will be done through a combination of tutorial-based assessment, class and group discussion and formal written assignments (20%) and a final examination (80%).
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of four tutorials, which test the students’ understanding of what they have learnt.
- completion of one written assignment/ project and one final quiz
- completion of the final closed book written examination
References for Prose
Abrams, M. H. (1986). The Norton Anthology of English Literature. (Fifth edition). New York: Norton & Company.
Armour, J. S. (1958). Standard English Essays. Bombay: Blackie and Son Ltd.
Boas, G. (1954). Modern English Prose. London: Macmillan & Co. Ltd.
Conlin, M.L. (1990). Patterns Plus: A Short Prose Reader with Argumentation. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company.
D’oyley, E. (1934). Modern Prose. London: Edward Arnold & Co.
Ridout, A. K. & Stuart, J. (1968). Short Stories for Discussion.NewYork: Charles Scribner’s.
Stafford, W. & Candelaria, F. (1966). The Voices of Prose. USA: McGraw. Hill, Inc.
References for Short Stories
Dolley, C. (1967). The Penguin Book of English Short Stories. Great Britain: Penguin Books Ltd.
Konigsberg, I. (1971) The Classic Short Story. U.S.A.: Harper and Row Inc.
Mizener, A. (1967). Modern Short Stories: The Uses of Imagination. U.S.A.: Norton & Company, Inc.
Chin, B. A. et. al. (2002). Glencoe Literature: The Reader’s Choice. U.S.A.: The McGraw-Hill Companies.
Ridout, A. K. & Stuart, J. (1968). Short Stories for Discussion. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons.
Eng 2106: English Literature – 8 (19th& 20th Century Poetry & Drama)
Course Description
This module deals with the study of a rich variety of poems, both British and American, which are representative of the century, being selected and presented in a thematic approach. Students will be able to appreciate the selected poems expressed in modern English so that their language power in speaking and writing will be enhanced.
This module also deals with selections from English Drama of 19th&20th centuries. Students will be able to read not only for pleasure but also to tackle conventional themes in the light of a new understanding of the theory and development of tragedy, comedy, and other modes of dramatic expression. It aims at helping students to develop their language through an intensive study of the style of writing in these plays, which introduce the on-setting element of modernism.
19th& 20th Century Poetry
- Stopping By Woods On A Snowy Evening Robert Frost
- It Is A Beauteous Evening, Calm And Free William Wordsworth
- A Slumber Did My Spirit Seal William Wordsworth
- The Splendour Falls On Castle Walls Alfred Tennyson
- Spring And Fall Gerard Manly Hopkins
- Loveliest Of Trees E. Housman
19th& 20th Century Drama
1. The Miracle Worker William Gibson
Learning Outcomes
After completion the course, students will be able to:
- acquire knowledge of culture-specific conventions of both British and American literatures
- appreciate the selected poems expressed in modern English so that their language power in speaking and writing will be enhanced
- analyze the functions of texts and their relations with historical, social and political contexts, and
- analyze how purpose, style and genre function in texts to achieve particular literary, rhetorical and aesthetic effects.
Assessment
Assessment will be done through a combination of tutorial-based assessment (20%), and a final closed book written examination (80%).
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- completion of tutorial-based assessment; group works, written assignments, poster competition/ role play and the presentations
- completion of final closed book examination
References for Poetry
Abrams, M. H. (1986) The Norton Anthology of English Literature. Vol. 1. USA: Norton and Company, Inc.
Hewett, R. P. (1984) A Choice of Poets: An Anthology of Poets from Wordsworth to the present day. UK: Nelson House.
Hoeper, Jeffrey D & James H. Pickering (1990) Poetry: An Introduction. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Peacock, W (1963) English Verse. Vol. V. Oxford: OUP
Pickering, James H. & Jeffrey D Hoeper (1986) Literature. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Ward, Thomas Humphry (1883) The English Poets. Vol. IV. London: Macmillan and Co.
Weekes, A. R (year not mentioned) The Odes of John Keats. London: University Tutorial Press Ltd.
Wilkie, Brian & James Hurt (1998) Literature of the Western World. Vol. I. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Wollman, Maurice (1948) Poems of Twenty Years: An Anthology. London: Macmillan and Co.
References for Drama
Abrams, M. H. (1986) The Norton Anthology of English Literature. Norton & Com. Inc
Alexander, Michael (2000) A History of English Literature. Macmillan Press Ltd.
Allison, Alexander W. et al. (1986) Masterpieces of Drama. Macmillan Publishing Co.
Pickering, James H. & Jeffrey D Hoeper (1986) Literature. USA: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Eng 2107: English Language Studies – 2 (Introduction to English Phonology)
Course Description
The module deals with two sub-disciplines in linguistics, namely phonetics and phonology. It also describes the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), English consonants and vowels, and phonemes. It focuses on the smallest of the superordinate units, the syllable and the phonological units above the syllable such as the phonetic characteristics of stress, stress position, segmental phonology of the phrase and word.
Contents
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Variation
- The International Phonetic Alphabet
- Describing English Consonants
- Describing Vowels
- Vowel phonemes
- Syllables: Phonology above the segment
- The word and above: Phonological unit above the syllable
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the module, students will be able to:
- classify levels of language structure
- describe English vowels and consonants
- indicate position of stress, and construct tree diagrams to show primary stress and secondary stress positions, and
- describe syllable and the phonological units above the syllable.
- apply knowledge of phonology in producing sounds
Assessment
Assessment will be done through a combination of tutorial-based assessment, class and group discussion and formal written assignments (20%) and a final examination (80%).
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of three tutorials, which test the students’ understanding of what they have learnt.
- completion of two written assignments
- completion of the final closed book written examination
References
McMahon, A. (2002) An Introduction to English Phonology. Edinburgh: EUP. Chapter 3, 6
Clark, J. & Yallop, C (1997). An Introduction and Phonetics and Phonology. UK: Blackwell Publishers Ltd. Chapter 1.
McMahon, A. (2002) An Introduction to English Phonology. Edinburgh: EUP. Chapter 1, 3, 6, 9, 10
Yule, G. (2006). The Study of Language. Cambridge: CUP. Chapter 5.
Eng- 2108: Communicative Skills -4
Course Description
This module aims to develop students’ communicative skills and language skills: grammar, vocabulary, reading, listening, speaking, pronunciation, critical thinking skills, problem solving skills and creativity. Authentic or semi-authentic reading and listening texts taken from a variety of text types will be used to develop their reading and listening skills. In the grammar section, students are encouraged to analyse and understand grammar through an inductive approach regarding examples in reading and listening texts and the vocabulary component pays attention to word building and lexical patterns and they are recycled through the speaking activities. The speaking section includes a variety of activities, which enable the students to comment on the topics and discuss the issues that arise, as well as talk about more personal experiences and knowledge, and the writing section will develop students’ writing through analysis of models and practice in producing different text styles.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the module, students will be able to:
- utilize the language phrases for giving presentations, describing and evaluating qualities in a real-life situation
- write argumentative essays, summary, and a questionnaire in a systematic way
- apply reading strategies: skimming, scanning, and proofreading
- use grammar patterns learned in real contexts
- develop their critical thinking skills, problem solving skills and creativity
Assessment
Assessment will be done through a combination of tutorial-based assessment, class and group discussion, formal written assignments, presentations and a final examination.
Students will be able to demonstrate the achievement of learning outcomes by:
- active participation in the class and group discussions for each lesson
- completion of six tutorials based on reading, writing, listening, speaking, vocabulary, and grammar.
- completion of individual written assignments and group presentation on a specific topic
- completion of the final closed book written examination
Prescribed Coursebook
Cotton, D., Falvey, D. & Kent, S. (2014). New Language Leader 2: Coursebook. England: Pearson Education Limited.
References
https://english-dashboard.pearson.com

