Post-graduate Diploma
PROGRAMME FOR (D.A.G) COURSES
For Economic and Mining Geology Specialization
Syllabus
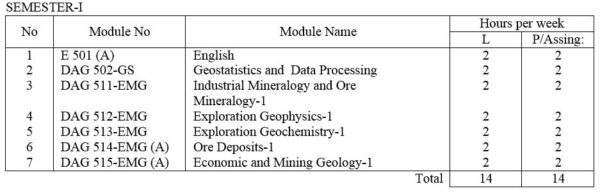
E 501(A) English: Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
DAG 502-GS Geostatistics and Data processing: Elementary Statistics, frequency distributions, mean, medium, mode and other measurements of distribution. Statistical decision theory. Correlation theory, Analysis of Multivariate data. Computer application in Applied Geology; Data collection and assessment ; Techniques for computer assisted analysis.
DAG 511-EMG Industrial Mineralogy / Ore Mineralogy – I
Fundamentals of the atomic structure of minerals; Mode of formation of minerals and ores in economic metallic and non-metallic minerals. Principles of X-ray diffractometry and the use of X-ray power cameras and diffractometer. Principles of S.E.M. and their application. Nature of reflected light. Ore features and their interpretation. Phase relations. Nature of reflected light. Ore textures and their measurements. Study of selected ores and ore mineral under microscope including textural studies.
DAG 512-EMG Exploration Geophysics – I : Review of the basics in electromagnetic, electromics and vector analysis. Density, magnetic, electrical, conductivity, solubility and other physical and chemical characteristics of common ore and gangue minerals, Introduction to I.P., resistivity, electromagnetic , magnetic, gravity, radiometric and seismic refraction methods, simple laboratory exercises.
DAG 513-EMG Exploration Geochemistry – I : Basic Principles. Field and analytical methods. Dispersion of elements ( secondary and primary ) and its applications in mineral exploration. Some mathematical and statistical methods applied in geochemical exploration. Laboratory exercises.
DAG 514-EMG(A) Ore deposits – I : Types of ore deposits and their geological and geochemical characteristics. Use of isotopic and fluid inclusion data. Genetic models for ore formation.
DAG 515-EMG(A) Economic and Mining Geology – I: General statement. Resources and reserves. Stages in mineral exploration. Mineral exploration techniques. Surveying for field geology. Drilling in mineral exploration. Exploration characteristics of ore deposits. Case studies. Laboratory exercises.
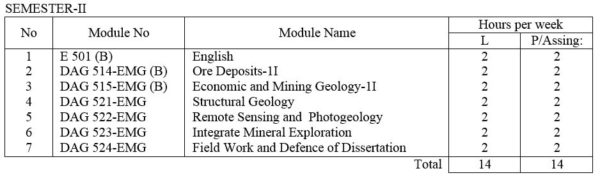
E 501(B) English: Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
DAG 514-EMG(B) Ore deposits – II: Major geological environments with respect to the plate tectonic hypothesis, and associated ore deposits, and their characteristics. Applications of ore genesis modeling in defining the exploration criteria for the various ore deposits.
DAG 515-EMG(B) Economic and Mining Geology – II : Sampling and valuation. Ore reserve calculations and grade controls. Mine surveying. Mining methods. Mineral dressing. Ore microscopy and extractive metallurgy. Marketing. Design and management in mineral exploration and development project. Environmental factors in mining industries.
DAG 521-EMG Structural Geology: Techniques of strain analysis and reconstruction of primary structures. Discussion of fracture patterns, shear zones, folding and boundinage. Statistical analysis of orientation data, superposed folding , domainal analysis of complex structures with practical work. Laboratory work of advanced subsurface methods and stereographic projection.
DAG 522-EMG Remote Sensing and Photogeology include lectures and laboratory exercises useful in mineral exploration and Applied Geology.
DAG 523-EMG Integrated Mineral Exploration ; Ore controls. Case studies of mineral exploration dealing with world and Myanmar examples.
DAG 524-EMG Field Work and Defense of Dissertation : Research works on assigned specialized Field; Preparation and defense of dissertation.
For Exploration Geophysics Specialization
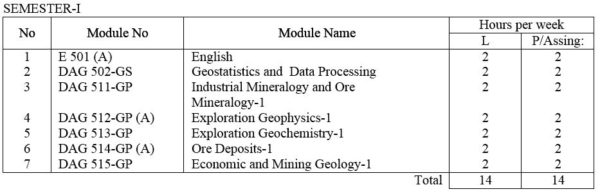
E 501(A) English: Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
DAG 502-GS Geostatistics and Data processing : Elementary Statistics, frequency distributions, mean, medium, mode and other measurements of distribution. Statistical decision theory. Correlation theory, Analysis of Multivariate data. Computer application in Applied Geology; Data collection and assessment ; Techniques for computer assisted analysis.
DAG 511-GP Industrial Mineralogy / Ore Mineralogy – I Fundamentals of the atomic structure of minerals; Mode of formation of minerals and ores in economic metallic and non-metallic minerals. Principles of X-ray diffractometry and the use of X-ray power cameras and diffractometer. Principles of S.E.M. and their application. Nature of reflected light. Ore features and their interpretation. Phase relations. Nature of reflected light. Ore textures and their measurements. Study of selected ores and ore mineral under microscope including textural studies.
DAG 512-GP (A) Exploration Geophysics – I : Review of the basics in electromagnetic, electromics and vector analysis. Density, magnetic, electrical, conductivity, solubility and other physical and chemical characteristics of common ore and gangue minerals, Introduction to I.P., resistivity, electromagnetic, magnetic, gravity, radiometric and seismic refraction methods, Simple laboratory exercises.
DAG 513-GP Exploration Geochemistry – I : Basic Principles. Field and analytical methods. Dispersion of elements (secondary and primary) and its applications in mineral exploration. Some mathematical and statistical methods applied in geochemical exploration. Laboratory exercises.
DAG 514-GP (A) Ore deposits – I: Types of ore deposits and their geological and geochemical characteristics. Use of isotopic and fluid inclusion data. Genetic models for ore formation.
DAG 515-GP Economic and Mining Geology – I: General Statement. Resources and reserves. Stages in mineral exploration. Mineral exploration techniques. Surveying for field geology. Drilling in mineral exploration. Exploration characteristics of oredeposits. Case studies. Laboratory exercises.
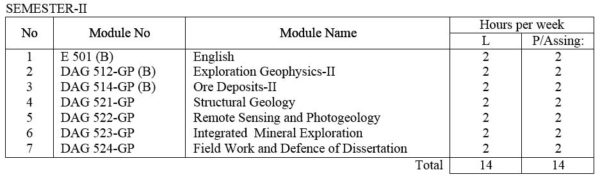
E 501(B) English: Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
DAG 512-GP(B) Exploration Geophysics – II : Geophysical methods in exploration includes review of introductory course, induced polarization (frequency and time domains), resistivity ( mapping and sounding), electromagnetic ( Turam, Slingram, V.L.F) , and their applications, field procedures, interpretation and limitations. Also includes magnetic, radiometric, gravity, seismic refraction, airborne and borehole methods; Integrated geophysical surveys and case histories. Laboratory exercises; Instrumentation.
DAG 514-GP (B) Ore deposits – II: Major geological environments with respect to the plate tectonic hypothesis, and associated ore deposits, and their characteristics. Applications of ore genesis modeling in defining the exploration criteria for the various ore deposits.
DAG 521-GP Structural Geology: Techniques of strain analysis and reconstruction of primary structures. Discussion of fracture patterns, shear zones, folding and boundinage. Statistical analysis of orientation data, superposed folding, domainal analysis of complex structures with practical work. Laboratory work of advanced subsurface methods and stereographic projection.
DAG 522-GP Remote Sensing and Photogeology include lectures and laboratory exercises useful in mineral exploration and Applied Geology.
DAG 523-GP Integrated Mineral Exploration; Ore controls. Case studies of mineral exploration dealing with world and Myanmar examples.
DAG 524-GP Field Work and Defense of Dissertation: Research works on assigned specialized field; Preparation and defense of dissertation.
For Exploration Geochemistry Specialization
E 501(A) English : Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
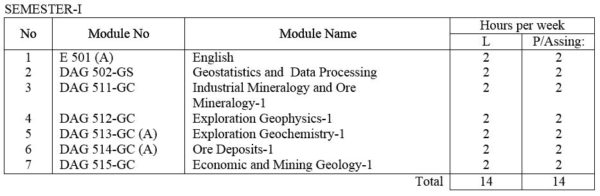
DAG 502-GS Geostatistics and Data processing : Elementary Statistics, frequency distributions, mean, medium, mode and other measurements of distribution. Statistical decision theory. Correlation theory, Analysis of Multivariate data. Computer application in Applied Geology; Data collection and assessment ; Techniques for computer assisted analysis.
DAG 511-GC Industrial Mineralogy / Ore Mineralogy – I Fundamentals of the atomic structure of minerals; Mode of formation of minerals and ores in economic metallic and non-metallic minerals. Principles of X-ray diffractometry and the use of X-ray power cameras and diffractometer. Principles of S.E.M. and their application. Nature of reflected light. Ore features and their interpretation. Phase relations. Nature of reflected light. Ore textures and their measurements. Study of selected ores and ore mineral under microscope including textural studies.
DAG 512-GC Exploration Geophysics – I : Review of the basics in electromagnetic, electromics and vector analysis. Density, magnetic, electrical, conductivity, solubility and other physical and chemical characteristics of common ore and gangue minerals, Introduction to I.P., resistivity, electromagnetic , magnetic, gravity, radiometric and seismic refraction methods, Simple laboratory exercises.
DAG 513-GC(A) Exploration Geochemistry – I : Basic Principles. Field and analytical methods. Dispersion of elements ( secondary and primary ) and its applications in mineral exploration. Some mathematical and statistical methods applied in geochemical exploration. Laboratory exercises.
DAG 514-GC(A) Ore deposits – I : Types of ore deposits and their geological and geochemical characteristics. Use of isotopic and fluid inclusion data. Genetic models for ore formation.
DAG 515-GC Economic and Mining Geology – I: General Statement. Resources and reserves. Stages in mineral exploration. Mineral exploration techniques. Surveying for field geology. Drilling in mineral exploration. Exploration characteristics of ore deposits. Case studies. Laboratory exercises.
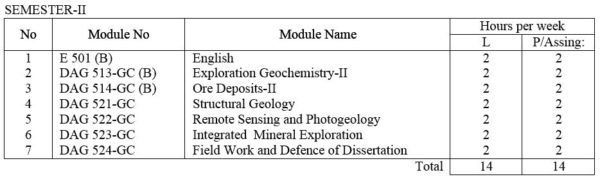
E 501(B) English: Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
DAG 513- GC(B) Exploration Geochemistry -II : Geochemistry of the earth. Detailed studies of soil science. Secondary and primary dispersion of elements. Systematic methods and procedures of geochemical exploration. Data processing and interpretation techniques. Review of exploration geochemistry in Myanmar. Seminars and laboratory exercises.
DAG 514-GC(B) Ore deposits – II: Major geological environments with respect to the plate tectonic hypothesis, and associated ore deposits, and their characteristics. Applications of ore genesis modeling in defining the exploration criteria for the various ore deposits.
DAG 521-GC Structural Geology: Techniques of strain analysis and reconstruction of primary structures. Discussion of fracture patterns, shear zones, folding and boundinage. Statistical analysis of orientation data, superposed folding , domainal analysis of complex structures with practical work. Laboratory work of advanced subsurface methods and stereographic projection.
DAG 522-GC Remote Sensing and Photogeology include lectures and laboratory exercises useful in mineral exploration and Applied Geology.
DAG 523-GC Integrated Mineral Exploration : Ore controls. Case studies of mineral exploration dealing with world and Myanmar examples.
DAG 524-GC Field Work and Defense of Dissertation : Research works on assigned specialized field; Preparation and defense of dissertation.
For Industrial Mineralogy and Ore Mineralogy Specialization

E 501(A) English: Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
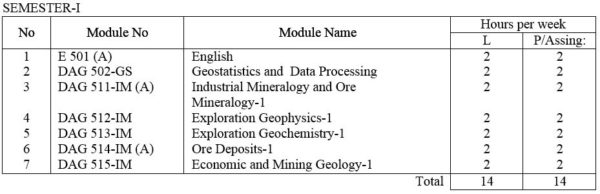
DAG 502-GS Geostatistics and Data processing : Elementary Statistics, frequency distributions, mean, medium, mode and other measurements of distribution. Statistical decision theory. Correlation theory, Analysis of Multivariate data. Computer application in Applied Geology; Data collection and assessment ; Techniques for computer assisted analysis.
DAG 511-IM (A) Industrial Mineralogy / Ore Mineralogy -I Fundamentals of the atomic structure of minerals; Mode of formation of minerals and ores in economic metallic and non-metallic minerals. Principles of X-ray diffractometry and the use of X-ray power cameras and diffractometer. Principles of S.E.M. and their application. Nature of reflected light. Ore features and their interpretation. Phase relations. Nature of reflected light. Ore textures and their measurements. Study of selected ores and ore mineral under microscope including textural studies.
DAG 512-IM Exploration Geophysics – I: Review of the basics in electromagnetic, electromics and vector analysis. Density, magnetic, electrical, conductivity, solubility and other physical and chemical characteristics of common ore and gangue minerals, Introduction to I.P., resistivity, electromagnetic , magnetic, gravity, radiometric and seismic refraction methods, Simple laboratory exercises.
DAG 513- IM Exploration Geochemistry – I : Basic Principles. Field and analytical methods. Dispersion of elements ( secondary and primary ) and its applications in mineral exploration. Some mathematical and statistical methods applied in geochemical exploration. Laboratory exercises.
DAG 514-IM(A) Ore deposits – I : Types of ore deposits and their geological and geochemical characteristics. Use of isotopic and fluid inclusion data. Genetic models for ore formation.
DAG 515-IM Economic and Mining Geology – I: General Statement. Resources and reserves. Stages in mineral exploration. Mineral exploration techniques. Surveying for field geology. Drilling in mineral exploration. Exploration characteristics of ore deposits. Case studies. Laboratory exercises.
E 501(B) English: Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
DAG 511-IM(B) Industrial mineralogy/ Ore Mineralogy – II : Advanced methods in mineralogy includes ore microscopy; X-ray diffraction; emission spectrography; differential thermal analysis; their basic principles, techniques, interpretation, limitations and practical applications.
Ore mineralogy includes crystal chemistry, principal mineral groups, native metals and semimetals, sulphides and sulphosalts, oxides. Industrial mineralogy includes abrasives, mineral pigments, glasses and enamels, ceramics and refractories, bonding materials, fillers and filters, single crystals, construction materials, metallurgical industry and commodities.
DAG 514-IM(B) Ore deposits – II: Major geological environments with respect to the plate tectonic hypothesis, and associated ore deposits, and their characteristics. Applications of ore genesis modeling in defining the exploration criteria for the various ore deposits.
DAG 521-IM Structural Geology: Techniques of strain analysis and reconstruction of primary structures. Discussion of fracture patterns, shear zones, folding and boundinage. Statistical analysis of orientation data, superposed folding , domainal analysis of complex structures with practical work. Laboratory work of advanced subsurface methods and stereographic projection.
DAG 522-IM Remote Sensing and Photogeology include lectures and laboratory exercises useful in mineral exploration and Applied Geology.
DAG 523-IM Integrated Mineral Exploration ; Ore controls. Case studies of mineral exploration dealing with world and Myanmar examples.
DAG 524-IM Field Work and Defense of Dissertation : Research works on assigned specialized field; Preparation and defense of dissertation.
For Gemmology Specialization
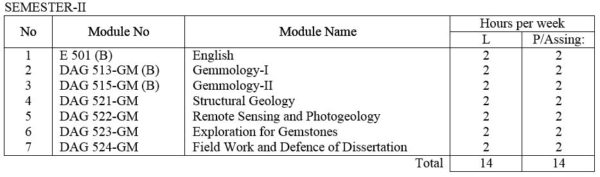
E 501(A) English: Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
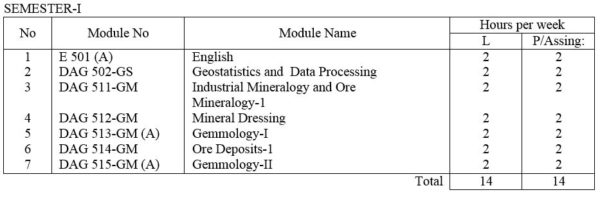
DAG 502-GS Geostatistics and Data processing : Elementary Statistics, frequency distributions, mean, medium, mode and other measurements of distribution. Statistical decision theory. Correlation theory, Analysis of Multivariate data. Computer application in Applied Geology; Data collection and assessment ; Techniques for computer assisted analysis.
DAG 511-GM Industrial Mineralogy / Ore Mineralogy – I Fundamentals of the atomic structure of minerals; Mode of formation of minerals and ores in economic metallic and non-metallic minerals. Principles of X-ray diffractometry and the use of X-ray power cameras and diffractometer. Principles of S.E.M. and their application. Nature of reflected light. Ore features and their interpretation. Phase relations. Nature of reflected light. Ore textures and their measurements. Study of selected ores and ore mineral under microscope including textural studies
DAG 512-GM Mineral dressing : Basic theory, comminution, liberation and grindability; conventional comminution equipments. Screening and classification; types of screen. Physical concentration process; gravity concetration; jigs, electronic and optical sorting; electrical and magnetic separation. Chemical concentration process; Leaching Cyanidation and amalgamation, Floatation: Liquid-solid separation: Flocation : Thickening, Filtration. Pollution control.
DAG 513-GM(A) Gemmology – I : Introduction to Gemmology : The nature of gemmology and gemstones,; classification of natural and artificial stones; Formation of minerals and types of occurrence of gems; Elementary crystal chemistry and crystallography ; Physical Properties; Units of Measurement; Nature of light.
DAG 514-GM Ore deposits – I : Types of ore deposits and their geological and geochemical characteristics. Use of isotopic and fluid inclusion data. Genetic models for ore formation.
DAG 515-GM(A) Gemmology-II: Optical Properties; Apparatus used in identification; Fashioning of gemstones; Description and elementary methods of identification of gems.
E 501(B) English: Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
DAG 513-GM(B) Advanced Gemmology – I : Crystal Chemistry and crystallography; Light and colour, Apparatus used in identificaion; Synthetic and imitation ( Simulant stones); Inclusion in Gemstones.
DAG 515-GM(B) Advanced Gemmology – II : Enhancement of Gemstone; Gem species (a) Inorganic Gems and (b) Organic products and their common simulants.
DAG 521-GM Structural Geology: Techniques of strain analysis and reconstruction of primary structures. Discussion of fracture patterns, shear zones, folding and boundinage. Statistical analysis of orientation data, superposed folding , domainal analysis of complex structures with practical work. Laboratory work of advanced subsurface methods and stereographic projection.
DAG 522-GM Remote Sensing and Photogeology include lectures and laboratory exercises useful in mineral exploration and Applied Geology.
DAG 523-GM Exploration for Gemstones: Application of Remote Sensing, Geochemistry, Geophysics and Geology. Extraction of Gemstones.
DAG- 524-GM Field Work and Defense of Dissertation : Research works on assigned specialized field; Preparation and defense of dissertation.
For Engineering Geology Specialization
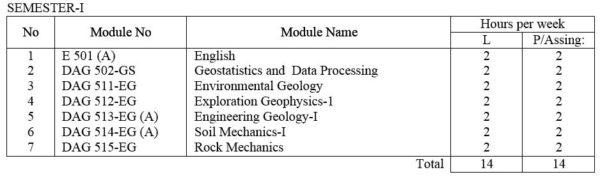
E 501(A) English : Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
DAG 502-GS Geostatistics and Data processing: Elementary Statistics, frequency distributions, mean, medium, mode and other measurements of distribution. Statistical decision theory. Correlation theory, Analysis of Multivariate data. Computer application in Applied Geology; Data collection and assessment ; Techniques for computer assisted analysis.
DAG 511-EG Environmental Geology : Introduction; Nature and aspects of various geologic hazards; Ways and means of mitigating these hazards; Proper use and care for Earth resources; Waste disposal problems.
DAG 512-EG Exploration Geophysics – I: Review of the basics in electromagnetic, electromics and vector analysis. Density, magnetic, electrical, conductivity, solubility and other physical and chemical characteristics of common ore and gangue minerals, Introduction to I.P., resistivity, electromagnetic , magnetic, gravity, radiometric and seismic refraction methods, Simple laboratory exercises.
DAG 513-EG(A) Engineering Geology – I : Scope and aim of engineering geology; Basic principles of engineering structures ; Geologic conditions for engineers.
DAG 514-EG(A) Soil Mechanics – I: Basic principles of soil mechanics; methods of testing soil properties.
DAG 515-EG Rock Mechanics: Basic Principles of rock mechanics. Interpretation of the geologic conditions concerning the safety of engineering structures, Studies made in the construction of the shafts, drifts, tunnels, mine pillars, rock foundations and slopes, etc.
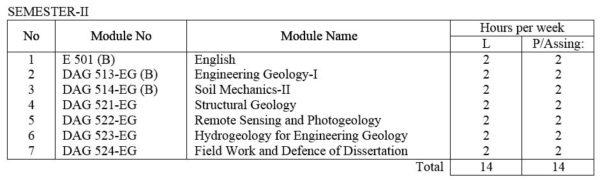
E 501(B) English: Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
DAG 513-EG(B) Engineering Geology – II : Selected topics in case histories and engineering geological problems. Site visit.
DAG 514-EG(B) Soil Mechanics – II: Continuation of DAG 4306-EG Various engineering problems, such as foundation settlement, slope stability, seepage and drainage.
DAG 521-EG Structural Geology: Techniques of strain analysis and reconstruction of primary structures. Discussion of fracture patterns, shear zones, folding and boundinage. Statistical analysis of orientation data, superposed folding , domainal analysis of complex structures with practical work. Laboratory work of advanced subsurface methods and stereographic projection.
DAG 522- EG Remote Sensing and Photogeology include lectures and laboratory exercises useful in mineral exploration and Applied Geology.
DAG 523- EG Hydrogeology for Engineering Geology: Basic principles of hydrogeology, Groundwater reservoirs, and hydrogeological exploration methods.
DAG 524- EG Field Work and Defense of Dissertation : Research works on assigned specialized field; Preparation and defense of dissertation.
For Hydrogeology Specialization
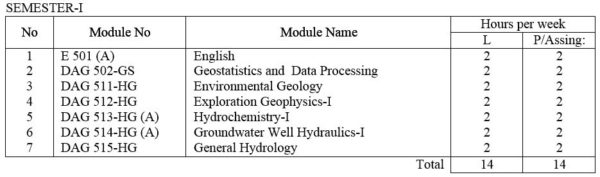
E 501(A) English: Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
DAG 502-GS Geostatistics and Data processing: Elementary Statistics, frequency distributions, mean, medium, mode and other measurements of distribution. Statistical decision theory. Correlation theory, Analysis of Multivariate data. Computer application in Applied Geology; Data collection and assessment ; Techniques for computer assisted analysis.
DAG 511-HG Environmental Geology :. Introduction; Nature and aspects of various geologic hazards; Ways and means of mitigating these hazards; Proper use and care for Earth resources; Waste disposal problems.
DAG 512-HG Exploration Geophysics -I: Review of the basics in electromagnetic, electronics and vector analysis. Density, magnetic, electrical, conductivity, solubility and other physical and chemical characteristics of common ore and gangue minerals, Introduction to I.P., resistivity, electromagnetic , magnetic, gravity, radiometric and seismic refraction methods, Simple laboratory exercises.
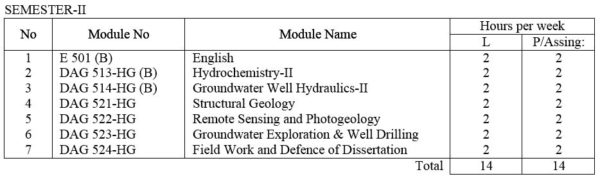
DAG 513-HG(A) Hydrochemistry – I: Principles of hydrogeochemistry. Chemical nature of groundwater, analysis and chemical classification.
DAG 514-HG(A) Groundwater Well Hydraulics – I: Basis of groundwater well hydraulics; hydraulics; hydraulic characteristics of rocks; aquifers and groundwater occurrence; hydraulic characteristics of aquifers.
DAG 515-HG General Hydrology : Hydrologic cycle, Measurement of precipitation, Evaporation & transipiration. Runoff and stream flow; Introduction to hydraulics; Pipe flow; Pumps and their characteristics.
E 501(B) English: Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
DAG 513-HG(B) Hydrochemistry- II: Continuation of DAG 513-HG. Salinity and alkalinity problems of soils with Myanmar examples, mineral factors, and hydrochemical dispersion of elements in groundwater.
DAG 514-HG(B) Groundwater Well Hydraulics – II : Continuation of DAG 514- HG. Methods of pumping test; aquifer boundaries and groundwater flownets; multiple well system; partially penetrating wells; and well spacing problems.
DAG 521-HG Structural Geology: Techniques of strain analysis and reconstruction of primary structures. Discussion of fracture patterns, shear zones, folding and boundinage. Statistical analysis of orientation data, superposed folding , domainal analysis of complex structures with practical work. Laboratory work of advanced subsurface methods and stereographic projection.
DAG 522-HG Remote Sensing and Photogeology include lectures and laboratory exercises useful in mineral exploration and Applied Geology.
DAG 523-HG Exploration methods and Regional Hydrogeology : Classification of aquifers for water supply; hydrogeologic investigation of groundwater for industry, irrigation, etc; hydrogeologic nature of dry zone region; and regional hydrogeology of Myanmar.
DAG- 524-HG Field Work and Defense of Dissertation : Research works on assigned specialized field; Preparation and defense of dissertation.
For Petroleum Geology Specialization

E 501(A) English: Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
DAG 502-GS Geostatistics and Data processing: Elementary Statistics, frequency distributions, mean, medium, mode and other measurements of distribution. Statistical decision theory. Correlation theory, Analysis of Multivariate data. Computer application in Applied Geology; Data collection and assessment ; Techniques for computer assisted analysis.
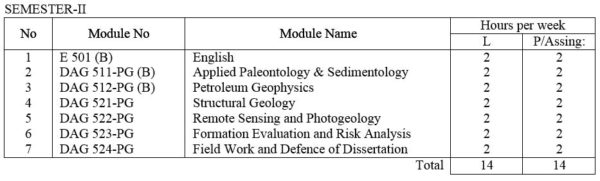
DAG 511-PG(A) Applied Paleontology: Morphology, Paleoecology, methods of sampling and preparation of various microfossil groups including foraminifera and spores; practical introduction to procedures in micropaleontological laboratories and biostratigraphical methods.
Sedimentology : Textures and structures of sediments; Petrology of sandstones and limestones; processes of deposition ; environmental and basin analysis.
DAG 512-PG(A) Exploration Geophysics – I: Review of the basics in electromagnetic, electromics and vector analysis. Density, magnetic, electrical, conductivity, solubility and other physical and chemical characteristics of common ore and gangue minerals, Introduction to I.P., resistivity, electromagnetic , magnetic, gravity, radiometric and seismic refraction methods, Simple laboratory exercises.
DAG 513-PG Petroleum Exploration : The search for hydrocarbon deposits has led to the development of subsurface branches of stratigraphy, micropaleontology, structural geology and exploration geophysics. This course introduces the student to the application and interaction of these four branches in the exploration for oil and gas.Source, reservoirs, traps, origin, migration, physical and chemical properties and distribution of petroleum, as well as conservation and utilization of hydrocarbon resources are discussed along with drilling, well logging, magnetic, gravity and seismic method. Laboratory work includes well-sample examination, subsurface contour mapping, sedimentary basin evaluation and electrical log correlation.
DAG 514-PG Log Interpretation : Application of electric logs, practical analysis of electrical, radioactivity and temperature Logs and interpretation, base upon their data. Estimation and evaluation of primary oil reserves.
DAG 515-PG Applied Petroleum Geochemistry : Concepts in Geochemistry, Sedimentation of organic matter, composition and structure of organic matter in Immature sediments, transformation of organic matter into Hydrocarbon, source rock character and types of organic matter, oil window area, Migration of hydrocarbon, oil in reservoir and Traps, Geochemical methods and tools in petroleum explorations, and methods to get require data for explorationist.
E 501(B) English: Technical English course intended to give the student enough ability to converse, to read periodicals and write technical reports.
DAG 511-PG(B) Applied Paleontology: Morphology, Paleoecology, methods of sampling and preparation of various microfossil groups including foraminifera and spores; practical introduction to procedures in micropaleontological laboratories and biostratigraphical methods.
Sedimentology : Textures and structures of sediments; Petrology of sandstones and limestones; processes of deposition ; environmental and basin analysis.
DAG 512-PG(B) Petroleum Geophysics : An advanced course in exploration with emphasis on the techniques and interpretation of seismic reflection measurements. Other topics include theory of selected logging methods, and dynamic gravity measurement. Laboratory assignment include computer processing of field data, and interpretation of problems.
DAG 521-PG Structural Geology: Techniques of strain analysis and reconstruction of primary structures. Discussion of fracture patterns, shear zones, folding and boundinage. Statistical analysis of orientation data, superposed folding , domainal analysis of complex structures with practical work. Laboratory work of advanced subsurface methods and stereographic projection.
DAG 522-PG Remote Sensing and Photogeology include lectures and laboratory exercises useful in mineral exploration and Applied Geology.
DAG 523-PG Formation Evaluation and Risk Analysis : Properties of reservoir rocks and fluids, Data evaluation for reservoir calculations water drive and solution gas drive, gas drive oil reservoirs, dissolved gas drive, gas cap drive and water drive oil reservoirs. Infection operations and water flooding process, Pressure maintenance.
DAG 524- PG Field Work and Defense of Dissertation : Research works on Oil field development ; Test well drilling; Cementing; Biostratigraphy and Risk Analysis in oil business; Preparation and defense of Dissertation.

