MSc Geology
REGIONAL GEOLOGY SPECIALIZATION
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER I
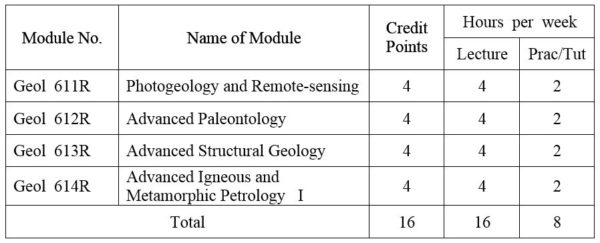
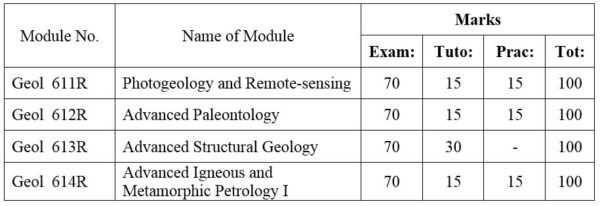
1.Module No: Geol 611R
Geomorphology with special reference to air-photo interpretation; Techniques of air-photo interpretation in geology; Air-photo interpretation of depositional landforms; Structural interpretation of air-photos; Sensor principles and capabilities, specific properties of images and records. Remote-sensing in geologic mapping; Remote sensing in Applied Geology; Remote sensing as an aid in development and the evaluation of natural hazards. Type of images and image processing methods.
2.Module No: Geol 612R
Micropaleontology; Ichnology; Conodonts
3.Module No: Geol 613R
Current trends in structural geology; Stress and strain in two dimensions; Behaviour of rock deformation; Rock behavior under experimental conditions; Dynamics of faulting; Analysis of macro-structures; Petrofabrics; Morphotectonics.
4.Module No: Geol 614R
Petrographic methods- a review; Modern classification and nomenclature of hard rocks; Genetic types of granitoids; Granitoid rocks of Myanmar; Metamorphic facies and facies series- a review; Metamorphic Epochs and Metamorphic Belts of Myanmar; Geochemical Cycles.
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER II
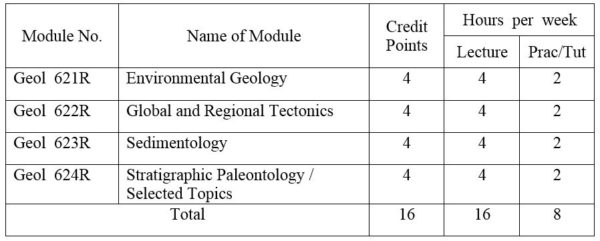
1.Module No: Geol 621R
Overview and general consideration; Nature and aspects of various geologic hazards:-hazards from earthquakes, hazards from volcanic eruption, hazards from ground failures, ways and means of mitigating these hazards; Earthquake prediction and control; Proper use and care for Earth resources:-groundwater resources, mineral resources, fossil fuel, soil; Geologic condition for proper waste disposal; Use of environmental potential maps in regional planning; Disaster Management and Risk Reduction.
2.Module No: Geol 622R
Recent advances in plate tectonics; Magmatism, metamorphism, sedimentation and metallogeny along different plate boundaries; Origin of marginal basins; Collision tectonics of India and Eurasia; Geodynamics of South-east Asia.
3.Module No: Geol 623R
Introduction and general consideration; Principles and problems of classification of sedimentary rocks; Clay minerals; Mud rocks; Turbidites, Flysch; Molasses; Sedimentation as ore genesis; Applied sedimentation.
Sedimentary environments and facies: – alluvial, deltaic, estuarine, clastic shoreline, carbonate platform, bathyal, abyssal, trench; Carbonate petrography; Carbonate microfacies analysis; Organism and sediments; Phosphate; Bedded chert.
4.Module No: Geol 624R
Stratigraphic invertebrate paleontology of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic rock sequences; Sedimentologic and stratigraphic application of selected groups of the invertebrates and microfossils; Depo-environments.
(OR)
Geology of the Moon; Mineral belts and mineral epochs of Myanmar; Mineralization at spreading centers; Quaternary stratigraphy of South-East Asia; Theory of evolution- a critical review; and other current topics.
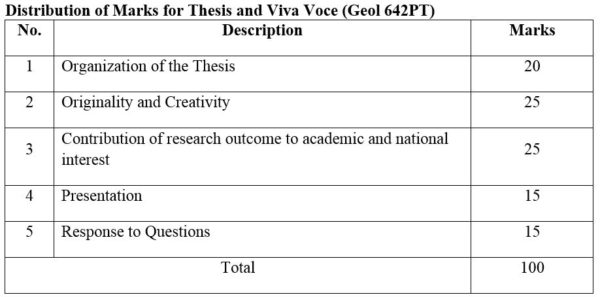
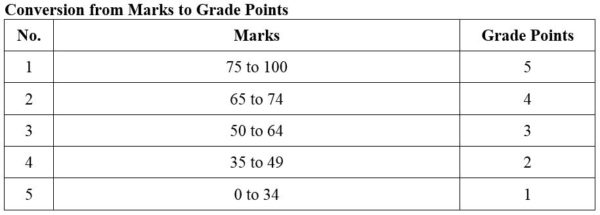
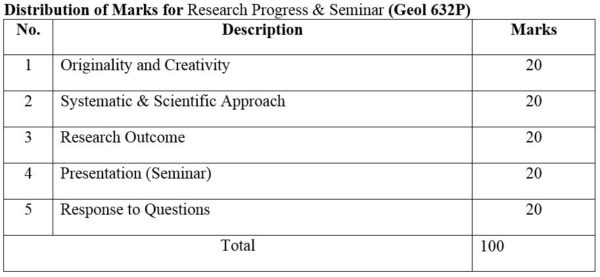
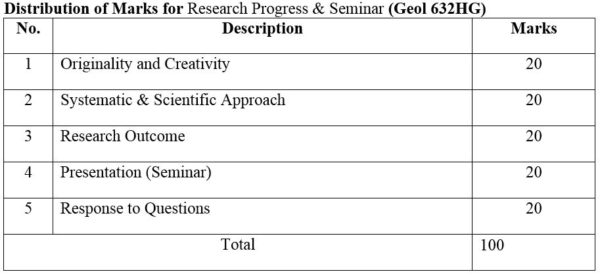
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS

SECOND YEAR SEMESTER I
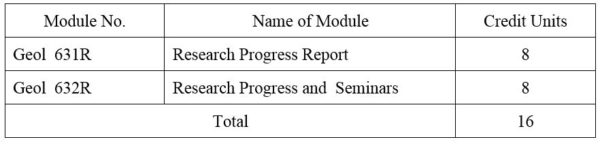
1.Module No: Geol 631R
2.Module No: Geol 632R
SECOND YEAR SEMESTER II

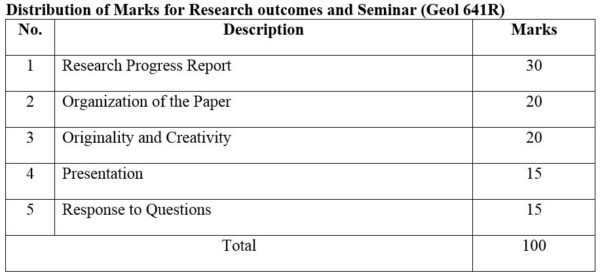
1. Module No: Geol 641R
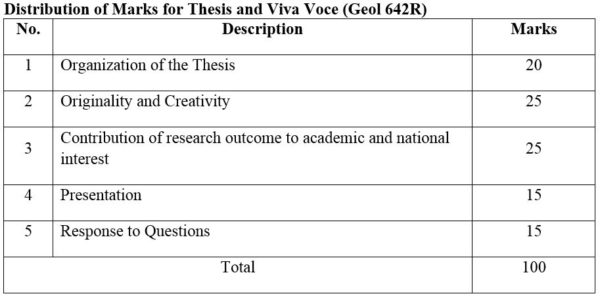
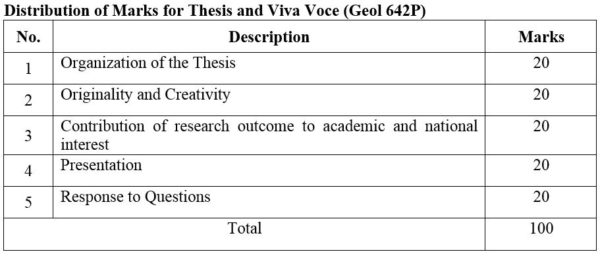
2.Module No: Geol 642R
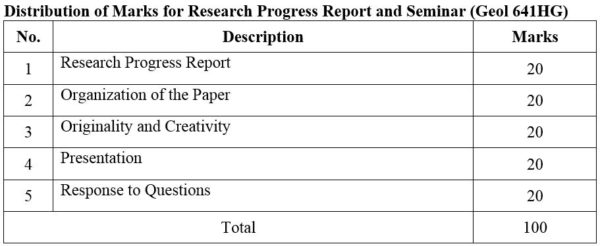
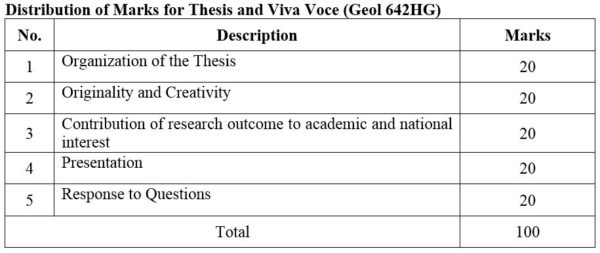
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS



PETROLOGY SPECIALIZATION
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER I
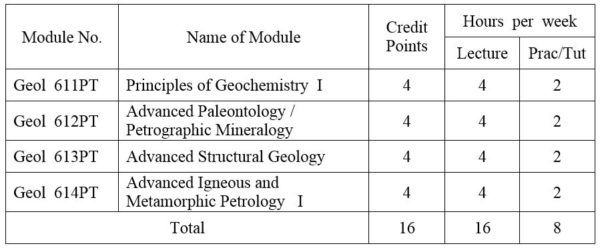
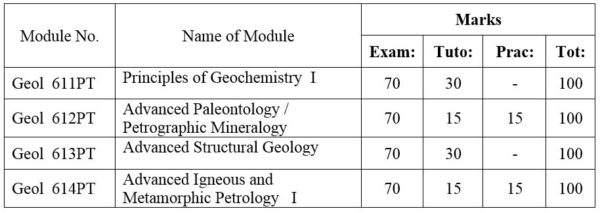
1.Module No: Geol 611PT
Abundance and geochemical classification of elements; Radioactivity and geochronology; Thermodynamics; Crystallization in igneous rocks melts.
2.Module No: Geol 612PT
Micropaleontology; Ichnology; Conodonts(OR) Orthoscopic and conoscopic studies of minerals; Review of silicate structure; Isomorphism and polymorphism in minerals; Solid solution in mineral groups; Systematic microscopic study of all important rock-forming mineral groups with emphasis on feldspar, pyroxene, micas ,aluminosilicates and garnets.
3.Module No: Geol 613PT
Current trends in structural geology; Stress and strain in two dimensions; Behaviour of rock deformation; Rock behavior under experimental conditions; Dynamics of faulting; Analysis of macro-structures; Petrofabrics; Morphotectonics.
4.Module No: Geol 614PT
Petrographic methods- a review; Modern classification and nomenclature of hard rocks; Genetic types of granitoids; Granitoid rocks of Myanmar; Metamorphic facies and facies series- a review; Metamorphic Epochs and Metamorphic Belts of Myanmar; Geochemical Cycles.
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER II
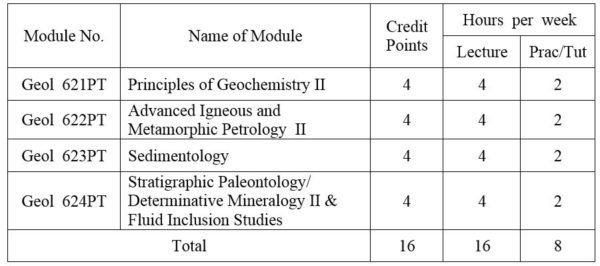
1.Module No: Geol 621PT
Element association in igneous rocks and minerals. Geochemistry of metamorphic processes; Sedimentary geochemistry; The hydrosphere; Atmosphere.
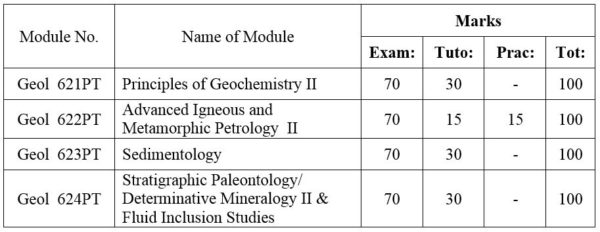
2.Module No: Geol 622PT
Historical development of petrology; Petrogenetic models; Experimental petrology and its uses; Origin of granitic and basaltic magmas; Magma association in relation to plate tectonic settings; Carbonatites; Metamorphism in relation to plate convergence.
3.Module No: Geol 623PT
Introduction and general consideration; Principles and problems of classification of sedimentary rocks; Clay minerals; Mud rocks; Turbidites, Flysch; Molasses; Sedimentation as ore genesis; Applied sedimentation.
Sedimentary environments and facies: – alluvial, deltaic, estuarine, clastic shoreline, carbonate platform, bathyal, abyssal, trench; Carbonate petrography; Carbonate microfacies analysis; Organism and sediments; Phosphate; Bedded chert.
4.Module No: Geol 624PT
Stratigraphic invertebrate paleontology of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic rock sequences; Sedimentologic and stratigraphic application of selected groups of the invertebrates and microfossils; Depo-environments.(OR) Scanning Electron Microscope:- General principles of Electron Microscopy; Image formation and electron diffraction; Sample preparation; Scattering of electrons by crystalline solids; Electron optical contrast phenomena. Electron Probe Micro-Analysis:- Instrumentation; The x-ray detection system; Sample preparation; Qualitative and quantitative analyses; Standards and calculation of correction factors; Some applications of the method in mineralogy. Introduction; Historical background of geothermometry; Origin of inclusions; Terms and terminology on fluid inclusions; Properties and characteristics of fluid inclusions. Types of inclusions; Instruments and methods of inclusion studies; Inclusion measurements and interpretation of measurements; Application of inclusion studies in various geologic environments; Future of inclusion studies.
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
SECOND YEAR SEMESTER I
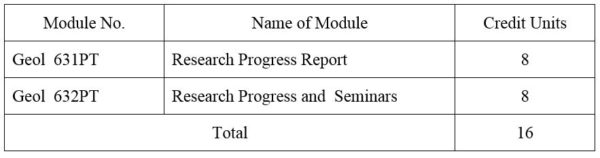
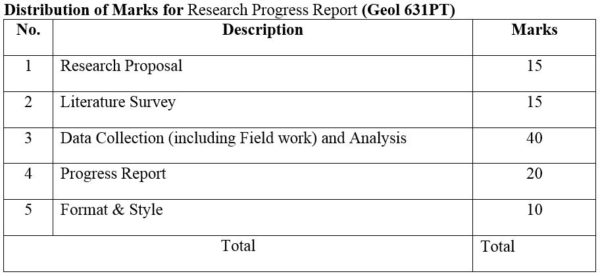
1.Module No: Geol 631PT
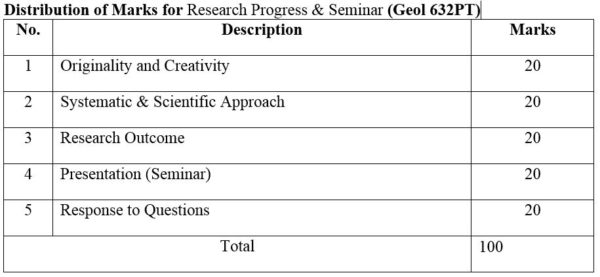
2.Module No: Geol 632PT
SECOND YEAR SEMESTER II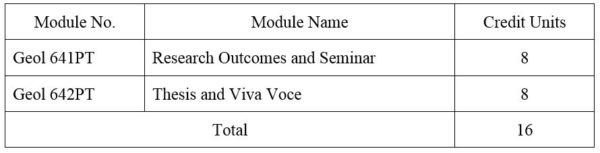
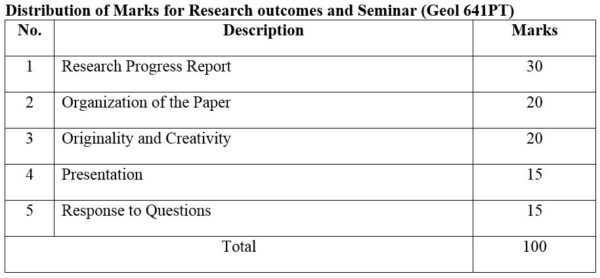
1. Module No: Geol 641PT
2. Module No: Geol 642PT
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
MINERALOGY SPECIALIZATION
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER I
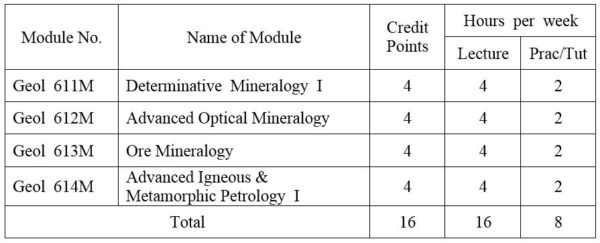
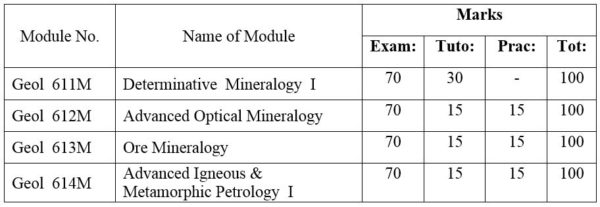
1.Module No: Geol 611M
Mineral separation techniques; Sampling and preparation; Separation by gravity; Magnetic separation; Miscellaneous methods. X-ray diffraction techniques; Classification of crystals; nature and generation of x-rays; The Laue Method; The powder method; Mineral identification.
2.Module No: Geol 612M
Orthoscopic and conoscopic studies of minerals. Uniaxial minerals; wave-velocity sufaces, optical indicatrix, interference figures, optic signs. Biaxial minerals; wave-velocity sufaces, optical indicatrix, interference figures, optic signs. Interference colors in relation to thickness and optical orientation; uses of colour chart. Optic orientation of biaxial minerals; construction of orientation diagram. Review of silicate structure; Isomorphism and polymorphism in minerals; Solid solution in mineral groups; Systematic microscopic study of all important rock-forming mineral groups with emphasis on feldspar, pyroxene, micas ,aluminosilicates and garnets. Principles and applications of Universal Stage.
3.Module No: Geol 613M
Ore microscopy (reflected light polarizing microscope); Physical and optical properties of ore minerals; Reflectivity method; Mineralogical analysis; Ore texture; Ore genesis; Description of important ore minerals (elements and intermetallic compounds, common sulphides and sulphates, oxidic ore minerals, gangue minerals).
4.Module No: Geol 614M
Petrographic methods- a review; Modern classification and nomenclature of hard rocks; Genetic types of granitoids; Granitoid rocks of Myanmar; Metamorphic facies and facies series- a review; Metamorphic Epochs and Metamorphic Belts of Myanmar; Geochemical Cycles
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER II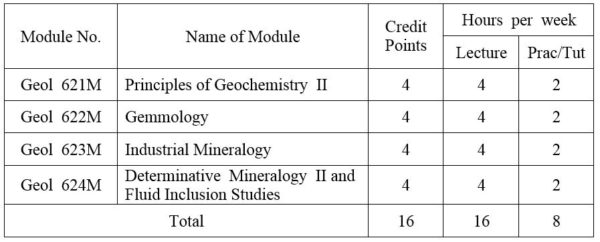
1.Module No: Geol 621M
Element association in igneous rocks and minerals. Geochemistry of metamorphic processes; Sedimentary geochemistry; The hydrosphere; Atmosphere.The Phase Rule and heterogeneous equilibrium- a review; important phase equilibrium; System of silicate melts and important metamorphic reactions; Application of these phase equilibrium and reactions in mineralogy.
2. Module No: Geol 622M
Introduction; Physical properties of gemstones; Light and related phenomena in gemstones; Colour in gemstones; Instruments used in gem testing; Fashioning of gemstones; Synthetic gemstones; Imitation and artificial treatments; Important gem species and their occurrences:- diamond, ruby and sapphire (corundum), emerald and aquamarine (beryl), spinals, garnets, topaz, tourmaline, chrysoberyl and alexandrite, dunburite, peridot, jadeite and nephrite jade, quartz and silica varieties, feldspars (moonstone, sunstone), pearls, corals, amber.
3.Module No: Geol 623M
Glasses, enamels and ceramic materials; Building materials; Phosphate and other mineral fertilizers; Mineral commodities (clay, feldspars, manganese minerals, etc).
4. Module No: Geol 624M
Scanning Electron Microscope:- General principles of Electron Microscopy; Image formation and electron diffraction; Sample preparation; Scattering of electrons by crystalline solids; Electron optical contrast phenomena; Electron Probe Micro-Analysis:- Instrumentation; The x-ray detection system; Sample preparation; Qualitative and quantitative analyses; Standards and calculation of correction factors; Some applications of the method in mineralogy. Introduction; Historical background of geothermometry; Origin of inclusions; Terms and terminology on fluid inclusions; Properties and characteristics of fluid inclusions. Types of inclusions; Instruments and methods of inclusion studies; Inclusion measurements and interpretation of measurements; Application of inclusion studies in various geologic environments; Future of inclusion studies.
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS

SECOND YEAR SEMESTER I
1.Module No: Geol 631PT
2.Module No: Geol 632PT
SECOND YEAR SEMESTER II

1. Module No: Geol 641PT
2. Module No: Geol 642PT
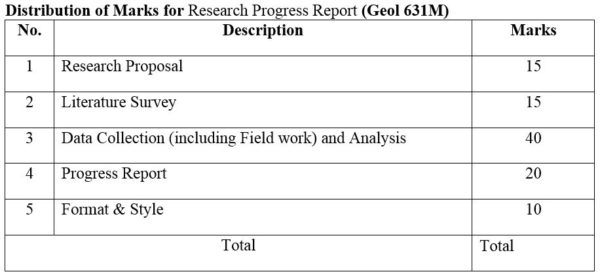
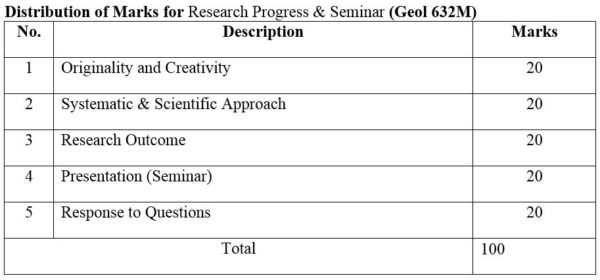
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
PALEONTOLOGY SPECIALIZATION
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER I
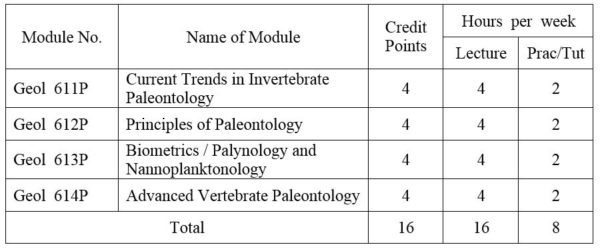
1.Module No: Geol 611P
Modern techniques in current research; mass extinction; Species and species problem; Conodonts. Methods of approach; Morphology and classification; Application of conodonts.
2.Module No: Geol 612P
Nature of fossil records and preservability of organic remains; Principles, practice and methods in description of a fossil specimen; Determination and description of ontogenetic variation; Variation in populations and population dynamics; Species, speciation, species problems, formal naming and description of species; Classification and taxonomy; General procedure and outline in identification of fossils; Modes, rates, trends and patterns of evolution, determination of phylogenetic relationships, and extinction.
3.Module No: Geol 613P
Biometrical methods in the study of invertebrate fossils; Introduction; The role of Biometrics in taxonomy; Basic statistical concepts; Population and sample in paleontology; Univariate analysis; Bivariate analysis: Statistical discrimination: Concepts of variability in bivariate samples. (OR)
Palynology:- Definition. Brief history; Sampling, processing and identification of faunas; Study of pollen assemblages; Determination of chronostratigraphic dating, formation representative and stratigraphic position; Determination of paleoenvironments. Nannoplanktonology:- Definition; Brief history; Methods of study; Sampling and preparation techniques; Identification of Nannofossils; Uses and advantages in application of Nannofossils; Age dating and interpretation of paleoenvironments; Ecology and comparison between forams and Nannofossils.
4.Module No: Geol 614P
Lower vertebrates :- Ostracoderms; Paleozoic fishes:- Placodermi and other groups; Aves:-earliest birds- ( birds of Mesozoic Era); Early reptiles:- marine reptiles, flying reptiles, land reptiles; Early Amphibian; Dinosaurs:- Sauropods, Theropods; Archiac mammals: Primitive mammals, mammals of Tertiary period. Primates:- Lower primates, higher primates, higher Anthropoid primates. Human Paleontology:- evolution of man (from Australopithecus to Homo Sapiens).
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER II
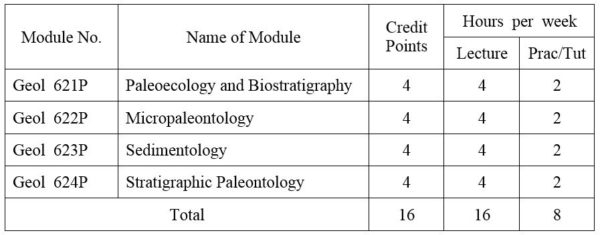
1.Module No: Geol 621P
Paleoecology: Scope; Methods and materials; Paleoautoecology and Synecology; Fossils and sediments association; Analysis and interpretation of paleo-depositional environments.
Biostratigraphy: Methods and approaches; Fossils as chronostratigraphic tools; Biochronology and evolution; Distribution of fossils in time and space; Paleoclimatological interpretation and paleogeographic aspects.
2.Module No: Geol 622P
Application of fossil foraminifera; extraction and processing of foraminifera; Classification; Paleoecology of fossil foraminifera: (a) Planktonic and (b) Benthonic larger foraminifera; Systematic study.
Application of fossil conodonts; extraction and processing of conodonts; Classification; Paleoecology of fossil conodonts.
3.Module No: Geol 623P
Introduction and general consideration; Principles and problems of classification of sedimentary rocks; Clay minerals; Mud rocks; Turbidites, Flysch; Molasses; Sedimentation as ore genesis; Applied sedimentation.
Sedimentary environments and facies:- alluvial, deltaic, estuarine, clastic shoreline, carbonate platform, bathyal, abyssal, trench; Carbonate petrography; Carbonate microfacies analysis; Organism and sediments; Phosphate; Bedded chert.
4. Module No: Geol 624P
Stratigraphic invertebrate paleontology of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic rock sequences; Sedimentologic and stratigraphic application of selected groups of the invertebrates and microfossils; Depo-environments.
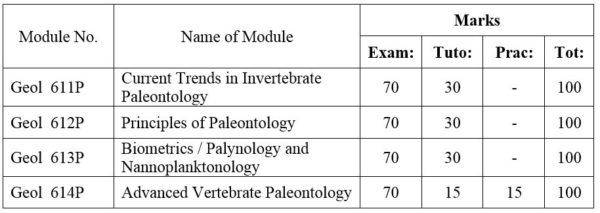
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS

SECOND YEAR SEMESTER I
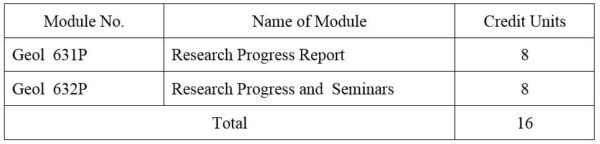
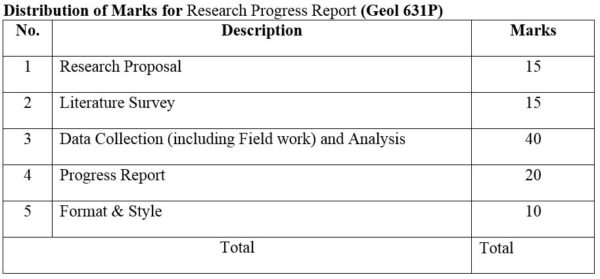
1.Module No: Geol 631P
2.Module No: Geol 632P
SECOND YEAR SEMESTER II

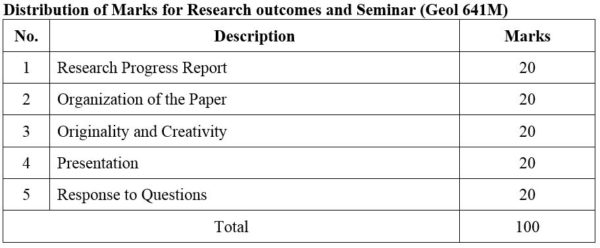
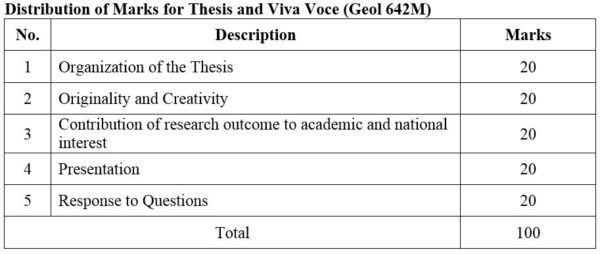
1. Module No: Geol 641P
2. Module No: Geol 642P
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS


ENGINEERING GEOLOGY SPECIALIZATION
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER I
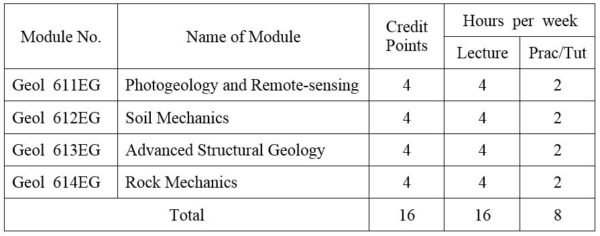
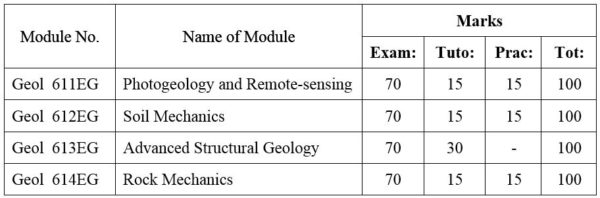
1.Module No: Geol 611EG
Geomorphology with special reference to air-photo interpretation; Techniques of air-photo interpretation in geology; Air-photo interpretation of depositional landforms; Structural interpretation of air-photos; Sensor principles and capabilities, specific properties of images and records. Remote-sensing in geologic mapping; Remote-sensing in Applied Geology; Remote sensing as an aid in development and the evaluation of natural hazards. Types of images and image processing methods.
Applied Geomorphology: Development of landforms. Relationship between landform and the underlying geology. Geomorphologic survey and analysis techniques.
2.Module No: Geol 612EG
Basic principles of soil mechanics; Index properties and soil classification; State of stress in soils; Stress-strain behaviour and shear strength; Effective stress concepts and permeability; Compressibility of soils; normally and overconsoildated soils; Soil compaction. Labiratory tests : Seieve analysis, Liquid limit, plastic limit and other index properties tests, Permeability tests, Triaxial tests, Diert shear test, Standard Proctor Test.
3. Module No: Geol 613EG
Current trends in Structural Geology. Stress and Strain in two dimensions. Behavior of rock deformation; Rock behavior under experimental conditions. Dynamics of faulting; Analysis of macro-structures. Petrofabrics. Morphotectonics. Global Tectonics (with special reference to recent developments).
4. Module No: Geol 614EG
Basic principles of rock mechanics; intact rock properties, rock mass and discontinuities, Deformability of rock mass; Rock slope engineering; basic mechanics of slope failures, Graphical presentation of geologic data, geological data collection, Shear strength of rock, Groundwater flow in rock mass, Plane failure, Wedge failure, circular failure, toppling failure.
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER II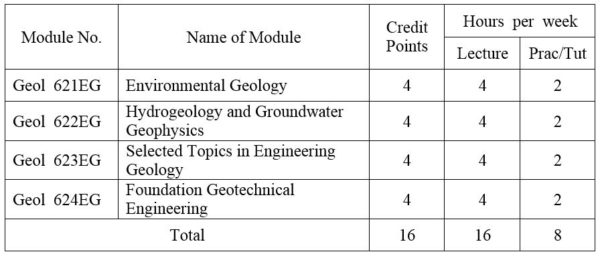
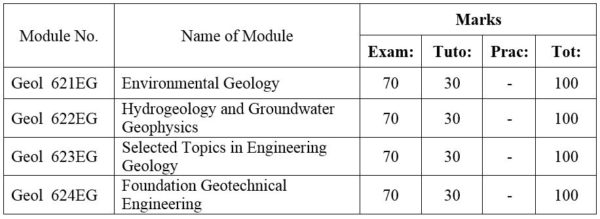
1.Module No: Geol 621EG
Geological hazards:- seismic risk, landslides, subsidence, floods, erosion, volcanic eruptions, discrete and continuous hazards; event return time, Geological resources and their management; Type of resources use and potential environmental conflict; Resource economic and policy formulation; Waste disposal and the mineral industry; Reclamation and rehabilitation of land used for extractive purposes:- Swamp drainage; Geology and Urban planning; Map preparation, Multiple land use principle, Aesthetic criteria for landscape evaluation. Environmental impact of dams, roads, explorative and extractive stages of mining; Impact statement techniques, Case studies; Disaster Management and Risk Reduction.
2. Module No: Geol 622EG
Current trends and aspects in advanced hydrogeology. Groundwater and Geotechnological problems.
Techniques and interpretation of shallow seismic refraction. Application of dam-site, highways, depth of weathering, material quality. Electrical Methods; Direct current geoelectric theory; resistivity sounding and profiling with applications to determination to bedrock depth, location of water table, sheared zones, etc. Magnetic, Electromagnetic and Gravity methods applied to engineering and hydrogeology problems; Various geophysical well loggings applied to determination of rock properties and location of clay-filled joints.
3. Module No: Geol 623EG
Subsurface exploration; Site investigation for dams; Highways and other engineering structures; Foundation analysis; Bearing capacity for shallow and deep foundation; Lateral earth pressure; Ground improvement methods; Tunneling; Disaster prevention and management; Earthquakes, Landslides etc.; Current trends and aspects in advanced geotechnology. Engineering Geology of Myanmar: Case-studies on Engineering Geology of dams, highway, bridge construction foundations etc. of Myanmar.
4. Module No: Geol 624EG
Foundation principles: Shallow and deep foundations (spread footing foundation, mat foundation, deep foundation, bearing capacity); Settlements (basic for design methods)
Foundation investigation for dams and other hydraulic structures; High way and airports, bridges, and building;
Seepage through dam foundation: Groundwater control methods; Cutoff trench, sheet piles, diaphragm walls and other methods of controlling seepages;
Foundation and engineering geology in hydropower development: Diversion type power development; Dam type power development;
Foundation Improvement: Grouting, Dental treatment, Rock anchors, and Load transfer;
Geology of tunnels and large underground openings; Foundations on unstable landforms and in seismically active regions
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
SECOND YEAR SEMESTER I
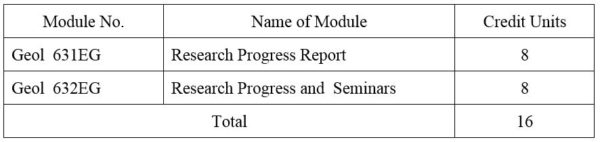
1. Module No: Geol 631EG
2.Module No: Geol 632EG
SECOND YEAR SEMESTER II
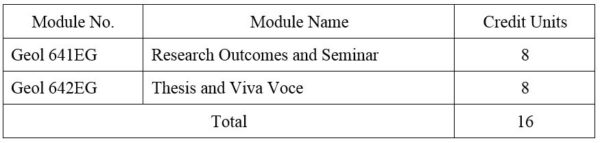
1. Module No: Geol 641EG
2. Module No: Geol 642EG
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS


PETROLEUM GEOLOGY SPECIALIZATION
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER I

1. Module No: Geol 611PG
Geomorphology with special reference to air-photo interpretation; Techniques of air-photo interpretation in geology; Air-photo interpretation of depositional landforms; Structural interpretation of air-photos; Sensor principles and capabilities, specific properties of images and records. Remote-sensing in geologic mapping; Remote-sensing in Applied Geology; Remote sensing as an aid in development and the evaluation of natural hazards. Types of images and image processing methods.
2. Module No: Geol 612PG
- The origin and formation of petroleum
- The nature of oil and gas
- Source rocks and reservoir rocks
- Hydrocarbon trap types and seal
- Petroleum exploration methods
- Well drilling and completion
- Subsurface geology (Well correlation , constructing cross-sections , subsurface geological maps)
- Wireline well logs (Electrical logs , Radioactivity logs, Sonic log)
- Improved and enhanced oil recovery methods
- Oil and Gas reserve
- Nonconventional petroleum resources (plastic and solid hydrocarbon, Tar sands , Oil shales, Coalbed methane, Shale gas)
- Petroleum System
3. Module No: Geol 613PG
Palynology: Definition. Brief history; Sampling, processing and identification of faunas; Study of pollen assemblages; Determination of chronostratigraphic dating, formation representative and stratigraphic position; Determination of paleoenvironments. Nannoplanktonology: Definition; Brief history; Methods of study; Sampling and preparation techniques; Identification of Nannofossils; Uses and advantages in application of Nannofossils; Age dating and interpretation of paleoenvironments; Ecology and comparison between forams and Nannofossils. (OR)
Current trends in Structural Geology. Stress and Strain in two dimensions. Behavior of rock deformation; Rock behavior under experimental conditions. Dynamics of faulting; Analysis of macro-structures. Petrofabrics. Morphotectonics. Global Tectonics (with special reference to recent developments).
4. Module No: Geol 614PG
Petroleum Geophysics: An advanced course in Petroleum Exploration with emphasis on the techniques and interpretation, GPS, GIS etc.; Laboratory assignments including computer processing of field data and interpretation of problems. Petroleum Geochemistry: Sample collections; Stratigraphy (rock units); Geostratigraphy laboratory analysis; Organic Analysis, TOC and type, Oil and Gas Analysis; Estimation of source rocks (Oil kitchen, Migration & trap); Estimation of oil in place; Risk Analysis.
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER II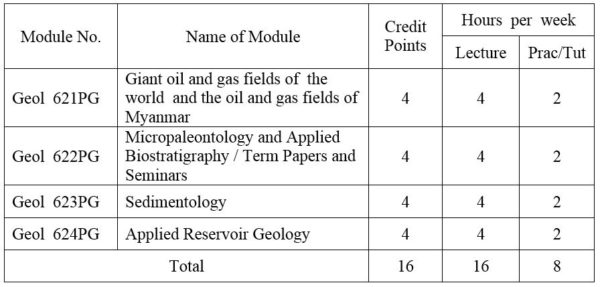
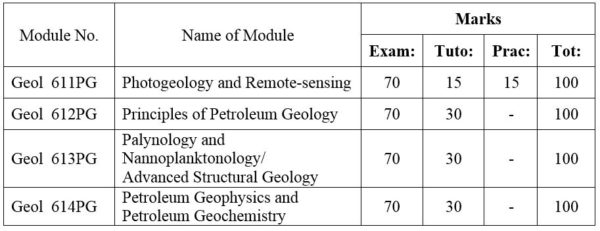
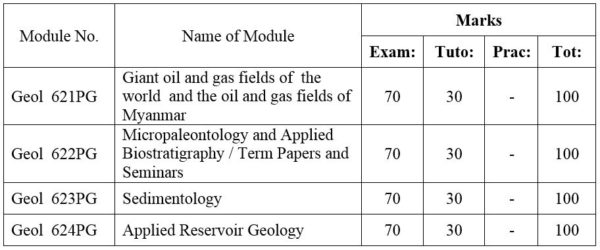
1. Module No: Geol 621PG
Selected topics on the reservoir geology of giant oil and gas field; Myanmar oil field and its economics.
2. Module No: Geol 622PG
Application of fossil Foraminifera; Extraction and processing of foraminifera; Classification; Paleoecology of fossil foraminifera: (a) Planktonic and (b) Benthonic larger foraminifera; Systematic study.
Methods and approaches; Fossils as chronostratigraphic tools; Biochronology and evolution; Distribution of fossils in time and space; Paleoclimtological interpretation and paleogeographic aspects; Current trends in Paleontology and Nannoplanktonology. (OR) Case studies of Petroleum Geology
3. Module No: Geol 623PG
Introduction and general consideration; Principles and problems of classification of sedimentary rocks; Clay minerals; Mud rocks; Turbidites, Flysch; Molasses; Sedimentation as ore genesis; Applied sedimentation.
Sedimentary environments and facies:- alluvial, deltaic, estuarine, clastic shoreline, carbonate platform, bathyal, abyssal, trench; Carbonate petrography; Carbonate microfacies analysis; Organism and sediments; Phosphate; Bedded chert.
4. Module No: Geol 624PG
Structural Mapping, Stratigraphy (Biozone & lithology), Well-log Analysis, Reservoir character (contour, fault, fault blocks, formation water analysis, Lab: data (porosity, Permeability, formation water); Oil & gas character in trap; Decline rate and risk analysis; Primary recovery and Secondary Process.
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
SECOND YEAR SEMESTER I
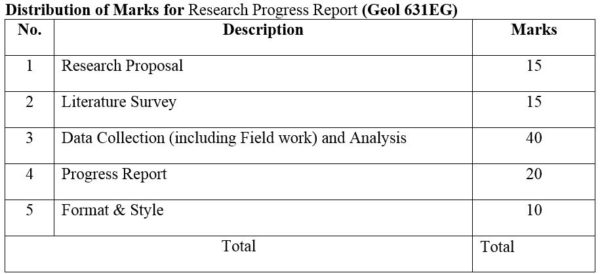
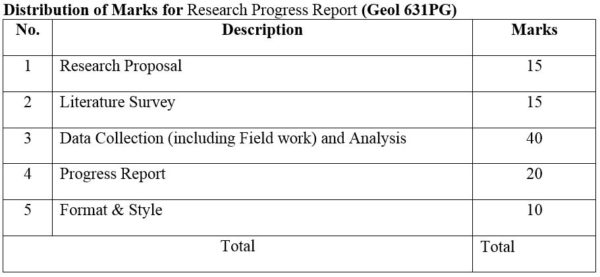
1. Module No: Geol 631PG
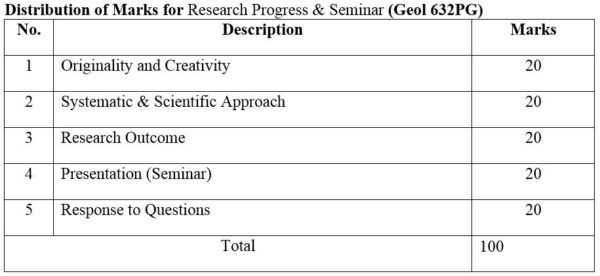
2. Module No: Geol 632PG
SECOND YEAR SEMESTER II
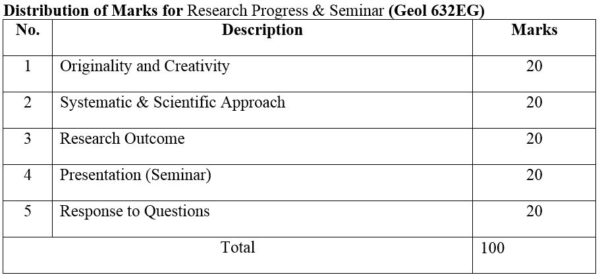
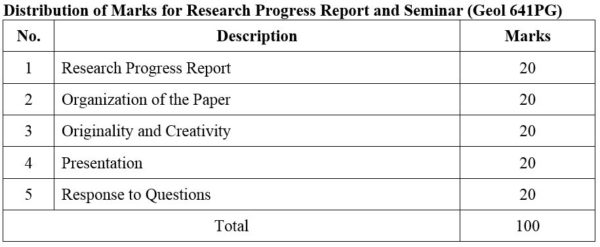
1. Module No: Geol 641PG
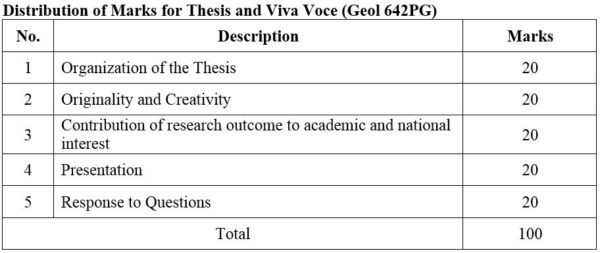
2. Module No: Geol 642PG
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
HYDROGEOLOGY SPECIALIZATION
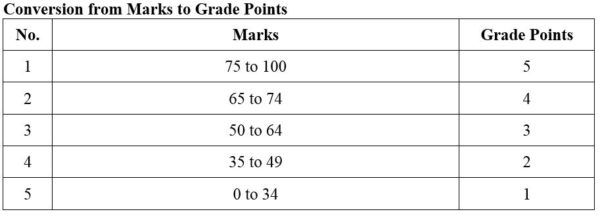
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER I
1. Module No: 611HG
Geomorphology with special reference to air-photo interpretation; Techniques of air-photo interpretation in geology; Air-photo interpretation of depositional landforms; Structural interpretation of air-photos; Sensor principles and capabilities, specific properties of images and records. Remote-sensing in geologic mapping; Remote-sensing in Applied Geology; Remote sensing as an aid in development and the evaluation of natural hazards. Types of images and image processing methods. Applied Geomorphology: Development of landforms. Relationship between landform and the underlying geology. Geomorphologic survey and analysis techniques.
2. Module No: Geol 612HG
Hydrologic cycle. Groundwater hydraulics. Hydrochemistry of groundwater. Recent advances in hydrogeology.
3. Module No: Geol 613HG
Current trends in Structural Geology. Stress and Strain in two dimensions. Behavior of rock deformation; Rock behavior under experimental conditions. Dynamics of faulting; Analysis of macro-structures. Petrofabrics. Morphotectonics. Global Tectonics (with special reference to recent developments).
4. Module No: Geol 614HG
Current trends and aspects in advanced hydrogeology. Groundwater and Geotechnological problems.
Hydrogeology of Myanmar: Case studies on Hydrogeology of Myanmar.
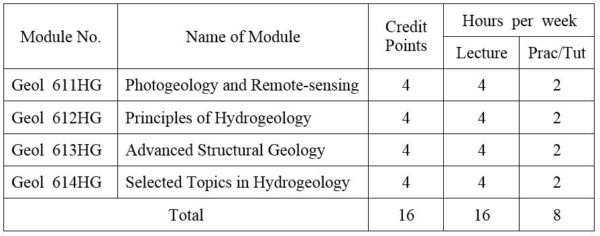
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER II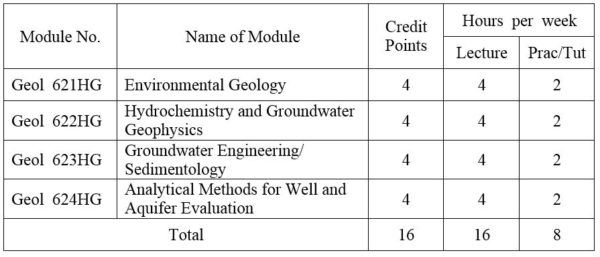
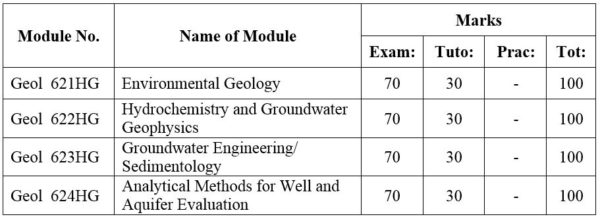
1. Module No: Geol 621HG
Geological hazards:- seismic risk, landslides, subsidence, floods, erosion, volcanic eruptions, discrete and continuous hazards; event return time, Geological resources and their management; Type of resources use and potential environmental conflict; Resource economic and policy formulation; Waste disposal and the mineral industry; Reclamation and rehabilitation of land used for extractive purposes:- Swamp drainage; Geology and Urban planning; Map preparation, Multiple land use principle, Aesthetic criteria for landscape evaluation. Environmental impact of dams, roads, explorative and extractive stages of mining; Impact statement techniques; Case studies; Disaster Management and Risk Reduction.
2. Module No: Geol 622HG
Sources of Salinity , Measures of Water Quality, Chemical Analysis, Graph Representations, Physical Analysis, Biological Analysis, Groundwater Samples, Water Quality Criteria, Changwgs in Chemical Composition, Dissolved Gases, Temperature, Saline Groundwater. Techniques and interpretation of shallow seismic refraction. Application of dam-site, highways, depth of weathering, material quality. Electrical Methods; Direct current geoelectric theory; resistivity sounding and profiling with applications to determination to bedrock depth, location of water table, sheared zones, etc. Magnetic, Electromagnetic and Gravity methods applied to engineering and hydrogeology problems; various geophysical well loggings applied to determination of rock properties and location of clay-filled joints.
3 . Name of Module: Groundwater Engineering (or) Sedimentology
Water Wells, Test Holes and Well Logs, Methods for Construction Shallow Wells, Methods or Drilling Deep Wells, Well Completion, Well Development, Testing Wells for Yield, Well Rehabilitation, Horizontal Wells. Concepts of Basin Management, Equation of Hydrologic Equilibrium, Groundwater Basin Investigations, Data Collection and Fieldwork, Alternative Basin Yields, Evaluation of Penennial Yield, Salt Balance, Basin Management by Conjunctive Use, Examples of Groundwater Management. (OR) Introduction and general consideration; Principles and problems of classification of sedimentary rocks; Clay minerals; Mud rocks; Turbidites, Flysch; Molasses; Sedimentation as ore genesis; Applied sedimentation. Sedimentary environments and facies:- alluvial, deltaic, estuarine, clastic shoreline, carbonate platform, bathyal, abyssal, trench; Carbonate petrography; Carbonate microfacies analysis; Organism and sediments; Phosphate; Bedded chert.
4. Module No: Geol 624HG
Evaluation of bounded aquifers, wedge-shaped and sloping aquifers, Anisotropic aquifers, Multi-layered aquifer systems and partial penetrating wells; well performance tests. Index properties and soil classification; Hydraulic conductivity.
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
SECOND YEAR SEMESTER I
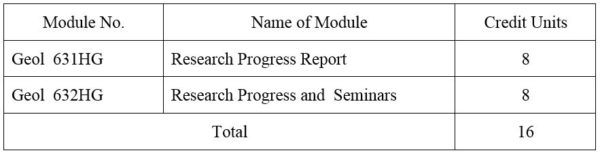
1. Module No: Geol 631HG
2. Module No: Geol 632HG
SECOND YEAR SEMESTER II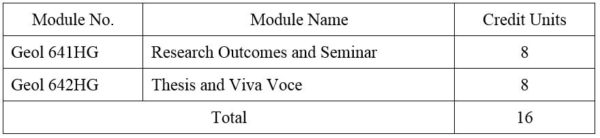
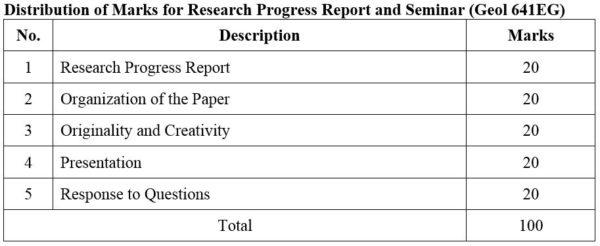
1. Module No: Geol 641HG
2. Module No: Geol 642HG
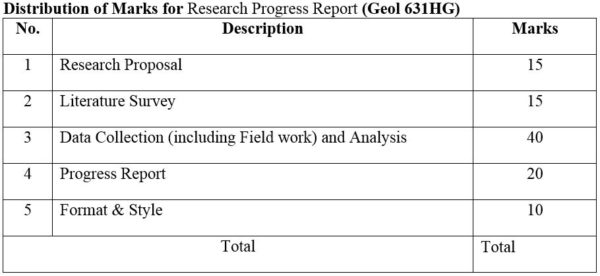
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS

ECONOMIC AND MINING GEOLOGY SPECIALIZATION)
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER I
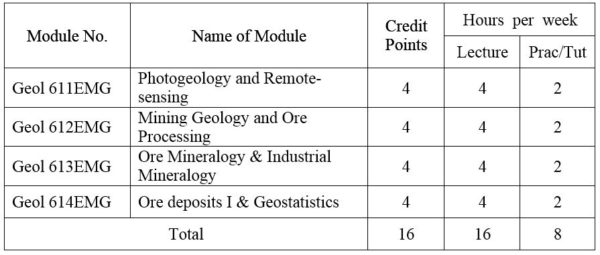
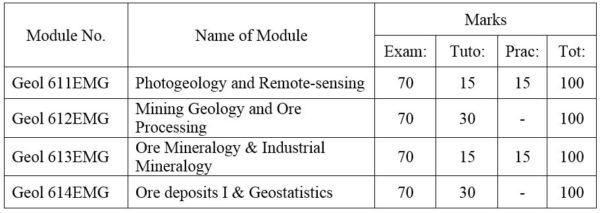
1. Module No: Geol 611EMG
Geomorphology with special reference to air-photo interpretation; Techniques of air-photo interpretation in geology; Air-photo interpretation of depositional landforms; Structural interpretation of air-photos; Sensor principles and capabilities, specific properties of images and records. Remote-sensing in geologic mapping; Remote-sensing in Applied Geology; Remote sensing as an aid in development and the evaluation of natural hazards. Types of images and image processing methods.
2. Module No: Geol 612EMG
Provides a basic introduction to mining. Includes the unique characteristics of the mining industry. Surface and underground mining methods and the unit operations of drilling, blasting, loading and haulage. Myanmar Mines Law is studied. Introduces the role of a mine geologist and the applications of geologic principles to mining practice. Underground and open pit mine mapping and solving of typical problems encountered in the mining industry. Covers mine sampling techniques and ore reserve estimation methods. Includes placer sampling and sampling of drill holes. Calculation of the tonnage factor, recovery, the concentration ratio and the value of the run of mine ore.
A general survey of mineral processing technology and topics include crushing, grinding, sizing, screening, thickening, classification, floatation and leaching.
3. Module No: Geol 613EMG
Ore Mineralogy: A detailed treatment of the ore minerals, their physical, chemical and optical properties, and their relation to each other in ores. Laboratory work includes the identification of minerals by optical, microchemical and X-ray methods, and study of paragenesis of mineral suites from selected mining districts of Myanmar.
Industrial Mineralogy: Glasses, enamels and ceramic materials; Building materials; Phosphate and other mineral fertilizers; Mineral commodities (clay, feldspars, manganese minerals, etc).
4. Module No: Geol 614EMG
The study of the styles, characteristics of metallic ore deposits. Theories of their origin and their implications related to known occurrences. Ore deposits models of the major types of deposits. The lecture series include detailed description of classical mining districts throughout the world.
Studies probability distributions, sampling distributions, estimation and hypotheses testing, regression and correlation.
FIRST YEAR SEMESTER II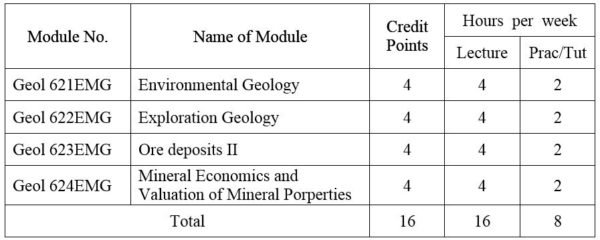
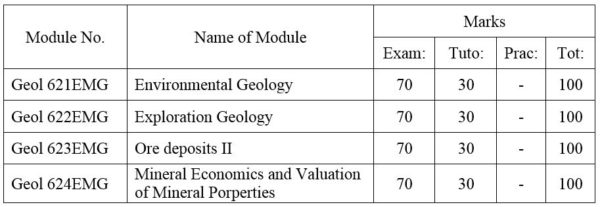
1. Module No: Geol 621EMG
Geological hazards:- seismic risk, landslides, subsidence, floods, erosion, volcanic eruptions, discrete and continuous hazards; event return time, Geological resources and their management; Type of resources use and potential environmental conflict; Resource economic and policy formulation; Waste disposal and the mineral industry; Reclamation and rehabilitation of land used for extractive purposes:- Swamp drainage; Geology and Urban planning; Map preparation, Multiple land use principle, Aesthetic criteria for landscape evaluation. Environmental impact of dams, roads, explorative and extractive stages of mining; Impact statement techniques; Case studies; Disaster Management and Risk Reduction.
2. Module No: Geol 622EMG
Exploration Geochemistry: Lectures deal with various geochemical environments, sample media, sample preparation, analytical methods, control of contamination and error problems. Laboratory work includes layout of exploration programs, sample collection and data analysis using geostatistical computer programs.
Exploration Geophysics: Studies methods of geophysical exploration with emphasis on the fundamental theory of measurement of the physical properties of the earth. The major methods used in geophysical prospecting and the instruments used are studied.
3. Module No: Geol 623EMG
A detailed study of the mining districts of Myanmar which includes the Bawdwin, Yadanatheingi and Bawsaing lead districts, Monywa and Shangalon porphyry copper deposits, the Mawchi tin lodes and the Kyaukpahto, Thabeikkyin and Pyinmana goldfields. Covers the occurrence, distribution, origin and economic importance of nonmetallic deposits. Studies the nonmetallic mining industry of Myanmar.
4. Module No: Geol 624EMG
Case studies on Economic Mineral Deposits of Myanmar
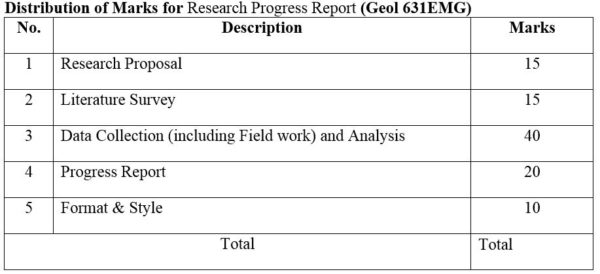
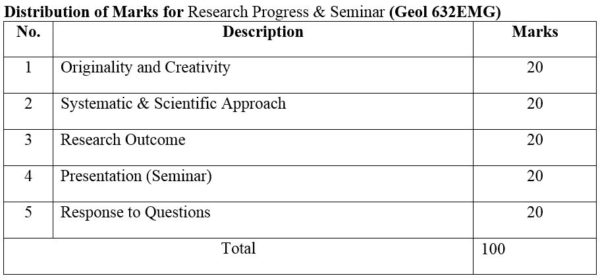
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
SECOND YEAR SEMESTER I
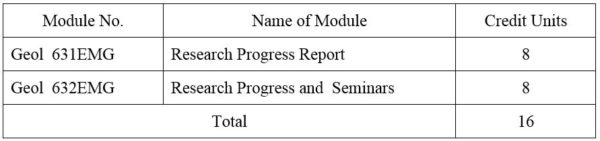
1. Module No: Geol 631EMG
2. Module No: Geol 632EMG
SECOND YEAR SEMESTER II
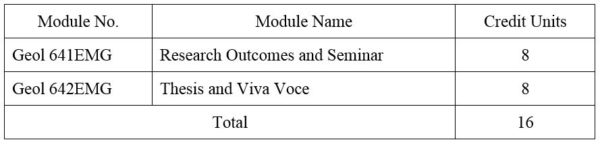
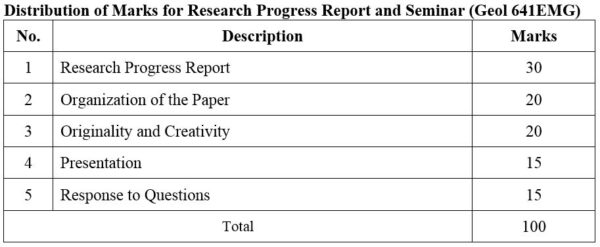
1. Module No: Geol 641EMG
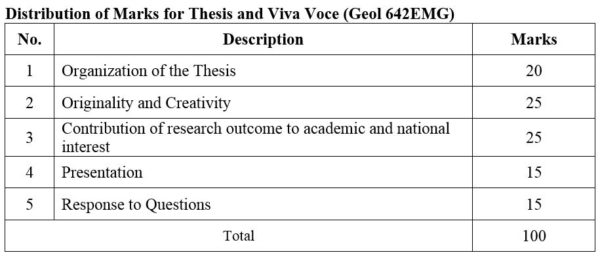
2. Module No: Geol 642EMG
DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS