Fourth Year
B.A Fourth Year (Semester I)
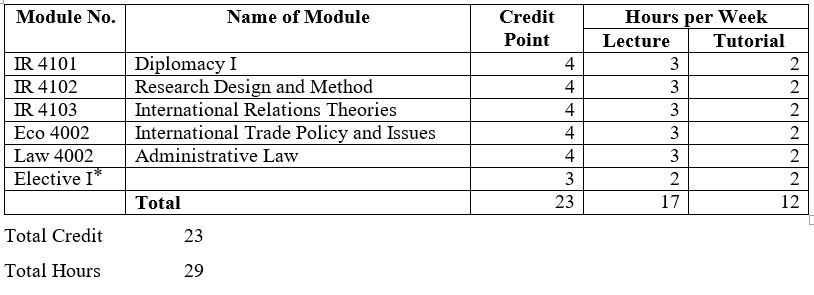
Core Courses
IR 4101 – (4) Diplomacy I
IR 4102 – (4) Research Design & Method
IR 4103 – (4) International Relations Theories
Eco 4001- (4) International Trade Policy and Issues
Law 4002 – (4) Administrative Law
Elective Courses
IR 4104 – (3) Governments and Politics of East Asia
IR 4105- (3) Myanmar-China Relations
A student must submit a research paper as a requirement for the degree of BA.
IR 4101 Diplomacy I
Course Description
This course aims to contribute the students for understanding the significance of diplomacy in international relations. It aims to focus on the evolution of diplomacy since civilization, role and functions of diplomacy in international relations. Diplomatic immunities, Cold War diplomacy, diplomacy in the 21st century, Functions of diplomatic mission and Ministry of Foreign Affairs will be studied in the course. Students will engage in group discussion, paper assignment and paper presentation for widening of their knowledge on diplomacy and quality of diplomat in international relations.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the semester, the students will be able
- to understand the changing trends of diplomacy in international relations
- to analyze the diplomacy of small powers and major powers for achieving their interests
- to enhance their knowledge on comprehensive role and functions of diplomacy in 21st century
Class Organization
The course is divided into 16 weeks. In each week, 3 hours will be devoted to interactive lectures and 2 hours will be assigned for group discussion and paper presentation.
Grading
Class work (presentation, assignment) 35
Final Exam paper 65
Final Exam
There will be final exam in Week 16. The final exam will be comprehensive (i.e., it will cover the entire semester) and be worth 65 % of the overall course grade.
Attendance and Presentation
Students will be assessed on their attendance in lectures, tutorials, assignments and their participation in group presentation in tutorial time. All class activities and attendance will be worth 35 % of the students overall final grade.
IR 4103 Theories of International Relations
Course Description
This course aims to analyze the important theories of International Relations. It will include four different types of International Relations theories such as Realism, Liberalism, Radicalism and Constructivism. The description on how to apply these theories in the issues of International Relations will also be presented.
Learning Outcomes
After ending the course, the students will assess
– to understand the basic concepts of theories of International Relations
– to criticize the differences of the Realism, Liberalism, Radicalism and Constructivism
– to explore the important of application of the International Relations Theories
Class Organization
This course is divided into 16 weeks. Three hours will be taken for the lecture time and two hours will be had for other class activities during each week.
Grading:
Exam Marks 65 marks
Class activity (attendance, discussion and assignment, etc.) 35 marks
Final Exam
After ending the semester, all course descriptions will be completed for the final exam which is worth 65 marks of the overall course grade.
Attendance and Presentation
Class participation (attendance, tutorial, discussion, presentation and assignment) is important for a student. Grade will be depended on the student’s activities. Plagiarism is strongly limited in the paper.
IR 4104 Governments and Politics of East Asia
Course Description
This course aims to provide the students with clear understanding of politics and governments of East Asians countries as well as some issues between and among them. In addition, it also aims the students at learning how these countries try to solve their issues and how to interact with one another and what the United States’ policy towards East Asia and Pacific will be explored as well. In this sense, we’d like to focus on the politics and governments of only four countries: Japan, two Korea and China although the East Asian region is made up of eight countries.
Learning outcomes
At the end of the semester, the students will be able
- to analyze comparatively the democratic politics of Japan and South Korea,
- to think about correlation between political system and economic development,
- to understand China’s foreign and security policy in East Asia
Class Organization
The course is divided into 16 weeks. In each week, 3 hours will be devoted to interactive lectures and 2 hours will be classwork
Grading
Class work (presentation, assignment, tutorial) 35
Final Exam paper 65
Final Exam
There will be final exam in Week 16. The final exam will be comprehensive (i.e., it will cover the entire semester) and be worth 65 marks of the overall course grade
Attendance and Presentations
Students will be assessed on their attendance in lectures and tutorials and for their participation in tutorial discussions, including group presentations in tutorial time. All tutorial activities and attendance will be worth 35% of the students overall final grade.
IR-4105 Myanmar-China Relations
Course Description
This course aims to provide students with a solid understanding of the situations of Myanmar-China Relations as a way of analysing Myanmar and China politics. Student will examine various determinant factors which influence and determine the Myanmar-China Relations. This course will provide students with critical thinking of various the dimensions, obstacles and opportunities in Myanmar-China Relations.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the semester, the students will be able
- to interpret the concept of Myanmar’s geopolitical situation
- to access China’s foreign policy and Myanmar’s foreign policy
- to examine the various dimensions of Myanmar-China Relations
- to analyse the challenges and opportunities of Myanmar-China Relations in the 21st
Class organisation
This course is divided into sixteen (16) weeks. In each week, two hours will be devoted to interactive lectures and two hours will be devoted to tutorials.
Readings
Readings from a variety of sources will be available to students through the course. The main textbooks will be “In the name of Pauk-Paw: Myanmar’s China Policy since 1948”, by Maung Aung Myoe and Modern China- Myanmar Relations: Dilemmas of Mutual Dependence, by David I. Steinberg and Hongwei Fan. Chapters from the book of Myanmar: Reintegrating into the International Community will also be used.
Grading
Attendance and Presentations 35%
Final Exam 65%
Attendance and Presentations
Students will be assessed on their attendance in lectures and tutorials and for their participation in tutorial discussions, including group presentations in tutorial time. All tutorial activities and attendance will be worth 35% of the students overall final grade.
Final Exam
There will be final exam in Week 16. The final exam will be comprehensive (i.e., it will cover the entire semester) and be worth 65% of the overall course grade.
B.A Fourth Year (Semester II)
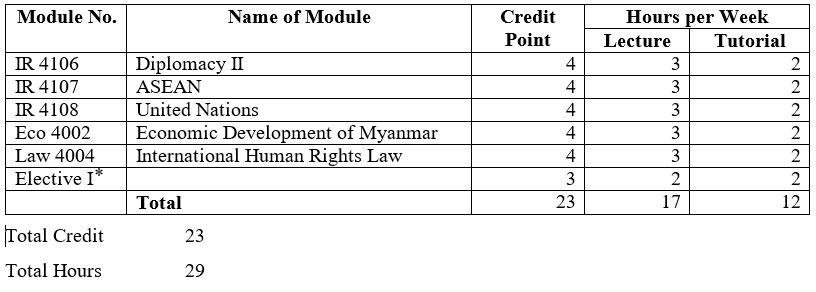
Core Courses
IR 4106 – (4) Diplomacy II
IR 4107 – (4) ASEAN
IR 4108 – (4) United Nations
Eco 4002- (4) Economic Development of Myanmar
Law 4004 – (4) International Human Rights Law
Elective Courses
IR 4109 – (3) Governments and Politics of South Asia
IR 4110 – (3) Myanmar-India Relations
A student must submit a research paper as a requirement for the degree of BA.
IR 4106 Diplomacy II
Course Description
This course aims to contribute the students for understanding the significance of diplomacy in international relations. It aims to focus on the art of negotiation and the instruments of foreign policy in international relations. The necessary arrangements for pre- negotiation and negotiation stages, difficulties and limitations for achieving the successful negotiations and the significant role of military strength and economic wealth in foreign policy formulation will be examined in the course. Students will engage in group discussion, paper assignment and paper presentation for widening of their knowledge on negotiation and international relations.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the semester, the students will be able
- to understand the problems and approaches for achieving a successful negotiation
- to analyze the instruments of foreign policy formulation with IR theories
- to promote the negotiation skills in dealing with their social and working environment
Class Organization
The course is divided into 16 weeks. In each week, 3 hours will be devoted to interactive lectures and 2 hours will be class work.
Grading
Class work (presentation, assignment) 35
Final Exam paper 65
Final Exam
There will be final exam in Week 16. The final exam will be comprehensive (i.e., it will cover the entire semester) and be worth 65 marks of the overall course grade
Attendance and Presentation
Students will be assessed on their attendance in lectures, tutorials, assignments and their participation in group presentation in tutorial time. All class activities and attendance will be worth 35 % of the students overall final grade.
IR 4107 ASEAN
Course Description
On regards with studying ASEAN, most of the students in Myanmar has developed a perception that ASEAN is a mere “Talk shop” or ASEAN is a semi-EU international institution. The reason is mainly because to understand ASEAN, it is to look from a new lens which is not the lens of Realism, through power or the lens of Liberalism, which is through benefits from cooperation, but from the lens of Constructivism, which emphasize on the reason why ASEAN came together and How they can build a Unity among diversity.
Learning Outcomes
After ending the course, the students will assess
– to understand the basic concepts of the ASEAN
– to criticize the non-interference principle of ASEAN
– to develop a theoretical concept on the progress of ASEAN
Class Organization
This course is divided into 16 weeks. Three hours will be taken for the lecture time and two hours will be had for other class activities during each week.
Grading:
Exam Marks 65 marks
Class activity (attendance, discussion and assignment, etc.) 35 marks
Final Exam
After ending the semester, all course descriptions will be completed for the final exam which is worth 65 marks of the overall course grade.
Attendance and Presentation
Class participation (attendance, tutorial, discussion, presentation and assignment) is important for a student. Grade will be depended on the student’s activities. Plagiarism is strongly limited in the paper.
IR 4108 The United Nations
Course Description
IR 4108 is a course that students will study about the history of the United Nations, its structure, main bodies and agencies and also challenges and opportunities that the UN faces in the 21st century. It also introduces students to the academic discussion about the role of the UN in the contemporary world politics. In this course students will examine the strength and weakness of UN in place of overcoming the global challenges. Moreover, students will consider that how does UN response to the pressure of globalization, and whether UN’s performances are converging with those of the Great Power countries and then can determine the positions of Great Powers in the international affairs. In addition, students are expected to be familiar with central theories of international relations regarding the UN and can also understand the unique position of the UN system in the world politics.
Learning Outcomes
By learning this course, the students will be able
– to understand the role of the United Nations in global politics
– to examine the achievements and weakness of UN’s performance in global challenges
– to criticize the impacts of UN’s intervention over some countries
Class Organization
This course is divided into sixteen weeks. In each week, three hours will be devoted to interactive lectures and two hours will be group discussion.
Grading
Tutorials 10%
Group Presentation & Assignment 25%
Final Exam 65%
Final Exam
The final exam will be comprehensive (i.e, it will cover the entire semester) and be worth 65% of the overall course grade. The exam will include materials from lectures, tutorials and discussion topics.
Presentation and Tutorials–Groups will be formed based on students’ portion and assigned topics for presentation. The presentation topics are based on course readings and outside research. Tutorials will include a range of lectures and will aim to increase student’s understanding of the weekly readings and key concepts. All tutorial activities and attendance will be worth 35% of the students overall final grade.
IR 4109 Governments and Politics of South Asia
Course Description
The aims of this course are to provide the students with clear understanding of politics and governments of South Asian countries as well as some issues between and among them. In addition, it also aims the students at learning how these countries try to establish their governments and politics and how to interact with one another will be explored as well. In this sense, we’d like to focus on the politics and governments of only Four countries: India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka although the South Asian region is made up of eight countries.
Learning outcomes
At the end of the semester, the students will be able
- to realize about good governance as prerequisite for rapid growth and sustained economic development,
- to help them think critically about democratic politics,
- to assess what is the best political system for their country
Class Organization
The course is divided into 16 weeks. In each week, 3 hours will be devoted to interactive lectures and 2 hours will be classwork.
Grading
Class work (presentation, assignment, tutorial) 35
Final Exam paper 65
Final Exam
There will be final exam in Week 16. The final exam will be comprehensive (i.e., it will cover the entire semester) and be worth 65 marks of the overall course grade.
Attendance and Presentations
Students will be assessed on their attendance in lectures and tutorials and for their participation in tutorial discussions, including group presentations in tutorial time. All tutorial activities and attendance will be worth 35% of the students overall final grade.
IR-4110 Myanmar-India Relations
Course Description
This course aims to provide students with a solid understanding of the situations of Myanmar-India Relations as a way of analysing Myanmar and India politics. Students will explore the importance of Myanmar-India Relations to implement the Indo-Pacific strategy. Student will examine various determinant factors which influence and determine the Myanmar-India Relations. This course will provide students with critical thinking of various the dimensions, obstacles and opportunities in Myanmar-India Relations.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the semester, the students will be able
- to interpret the concept of Myanmar’s geopolitical situation
- to access India’s foreign policy and Myanmar’s foreign policy
- to examine the various dimensions of India-Myanmar Relations
- to analyse the challenges and opportunities of India-Myanmar Relations under the Indo-Pacific strategy
Class organisation
This course is divided into sixteen (16) weeks. In each week, two hours will be devoted to interactive lectures and two hours will be devoted to tutorials.
Readings
Readings from a variety of sources will be available to students through the course. The main textbooks will be India-Myanmar Relations: Changing Contours, by Rajiv Bhatia and India-Myanmar Relations: Historical Links to Contemporary Convergences, by Lipi Ghosh and other authors. The related Articles will also be used.
Grading
Attendance and Presentations 35%
Final Exam 65%
Attendance and Presentations
Students will be assessed on their attendance in lectures and tutorials and for their participation in tutorial discussions, including group presentations in tutorial time. All tutorial activities and attendance will be worth 35% of the students overall final grade.
Final Exam
There will be final exam in Week 16. The final exam will be comprehensive (i.e., it will cover the entire semester) and be worth 65% of the overall course grade.

