Core Courses of Bachelor of Science
Undergraduate Studies
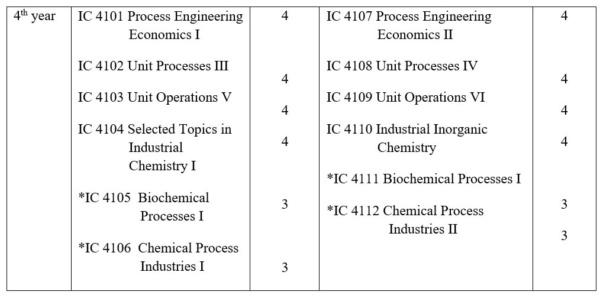
Core Courses of Bachelor of Science in Industrial Chemistry (Four-year Program, Total Credit Units 168)


* Elective courses
This is industrial chemsitry in yangon university.
# In partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the Bachelor of Science in Industrial Chemistry degree, Fourth Year Students must take part in occasional field trips (to plants / factories) / project assignments, related to their field of studies, as deemed necessary by the Department of Industrial Chemistry and Submission of Term Paper at the end of the second semester.
First Year
Course Description
Industrial Chemistry I (Organic and Analytical Chemistry)
This module includes the structure and nomenclature of organic compounds and the fundamental principles of organic chemistry. It provides the basic concept of analytical chemistry and is also extended to acquire skills in various analytical techniques.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the fundamental principles and concepts related to Organic and Analytical Chemistry.
-Identify the organic compounds based on their functional groups.
-Apply these principles and concepts in the synthesis and processing of organic compounds.
-Analyze physical and chemical properties, methods of preparation, behavior of solutions and titration indicators.
-Solve the problems related to the calculation of acid base titration.
-Manipulate the Organic and Analytical experiments.
Industrial Chemistry II (Inorganic and Physical Chemistry)
This module provides concepts and principles in the synthesis and methods of processing. This unit deals with the study of different methods to analyze physical and chemical properties, behavior of gases, equilibrium constant. Moreover it can also study the operations and equipment for extraction of minerals and ores.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the fundamental principles and concepts related to basis chemistry of gases and liquids, colloids.
-Understand colloidal systems for industrial or technological interest.
-Analyze physical and chemical properties, behavior of gases, equilibrium constant.
-Manipulate the acid/base radicals and physical experiments.
-Identify the structure and configuration of atom, nature and energy of electron.
-Classify the position of metals and non-metals in the periodic table and their occurrence, extraction methods and application.
-Understand the methods of exploration, mining and concentrating of the ores, refining of metals and its processing.
Second Year
Course Description
Industrial Organic Chemistry I
This module aims to introduce the naming system, and physical and chemical properties of aromatic, heterocyclic compounds and natural products. This module includes the isolation techniques, preparation and physical and chemical properties of different types of industrially important derivatives.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the naming system of aromatic and heterocyclic compounds and their derivatives, the sources and pathways of preparation process.
-Apply the isolation techniques for extraction of alkaloids from plant materials.
-Categorize the physical and chemical properties of different types of carbohydrates, the preparation of different products (food and industrially important derivatives).
-Understand the types of amino acid and its nomenclature, physical and chemical properties, structure of amino acids and proteins.
Unit Operations I and II
This module aims to introduce industrial equipment for chemical processes, basic fluid dynamics and characteristics of different types of fluid flow. It provides the fundamentals of solid processing operation. This unit also involves fundamental principles and concepts related to calculation of mass and energy balances in heat exchangers, steam boilers and evaporators.
Learning Outcomes
Unit Operations I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand fundamental units, Dimensional Analysis, Process Development and Industrial Equipment for Chemical Processes.
-Understand the fundamental principles of flow of fluids, size separation, size reduction and sedimentation.
-Apply these mechanisms and principles in industrial engineering.
Unit Operations II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the fundamental principles and concepts related to calculation of heat balances.
-Apply these concepts and principles in the analysis of specified systems.
-Understand the mechanism of heat exchangers, steam boilers and evaporators.
-Analyze the material and energy balances in heat exchangers, boilers and evaporators.
Industrial Stoichiometry
This module aims to introduce chemical engineering calculations. This unit is also extended to the development of mass and energy balances as applied to the wide range of chemical processes such as distillation columns, evaporators and reactors.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the fundamental principles and concepts related to calculation of mass and heat balances in distillation and evaporation.
-Analyze the systems of heat transferred and mass transferred across the boundary.
-Derive the appropriate mass and energy balance equations for a giving system.
Learning Outcomes
Industrial Physical Chemistry I
This module deals with the basic concepts and criteria of thermodynamic, phase rule and catalysis. It also involves energy transfer for closed and control volume systems, the interpretation and application of binary phase diagrams and also the important of catalyst in a chemical reaction and their effects on reaction rate.
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the basic concepts of chemical thermodynamic such as temperature, pressure, system, properties, process, state, cycles, equilibrium, enthalpy and entropy.
-Understand the first law, second law and third law of thermodynamics.
-Know heat effect, thermodynamics properties of fluids and flow process.
-Understand the principles of binary phase diagrams.
-Interpret and apply the process conditions.
-Study the importance of catalyst in a chemical reaction and their effects on reaction rate.
-Apply thermodynamics concepts in analyzing the thermal efficiencies of heat engines such as Carnot cycles and the coefficients of performance for refrigerators.
Fuel Science and Technology
This module gives an overview of coal and petroleum industry. It includes the origins, types and qualities of coal and petroleum and their refining as well as introduction to biofuels.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the fundamental concepts, production, purification and combustion mechanism of fossil fuels (solid, liquid and gaseous).
-Classify the fuels according to their phase state as solid, liquid and gaseous and according to their properties.
-Apply the laboratory tests for the analysis of coal to assess its properties.
-Solve the problems related to combustion of fuel used in chemical process industries.
Third Year
Course Description
Water and Wastewater Technology I & II
This module aims to introduce the general knowledge of natural waters, water characteristics and treatment of water and wastewater. This unit also provides the natural water resources and water quality standards for boiler feed water, surface and ground water, and wastewater.
Learning Outcomes
Water and Wastewater Technology I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Identify the physical, chemical and biological parameters of the surface and ground water.
-Calculate the chemical parameters such as alkalinity and hardness.
-Recognize the water quality standards.
-Illustrate the fundamentals of water, boiler feed water and wastewater treatment.
-Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of softening and aeration.
-Gain knowledge on disinfection of water.
-Manipulate the experiments of water analysis.
Water and Wastewater Technology II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Describe and demonstrate basic knowledge of key principles underlying disinfection, coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation and filtration of water and wastewater.
-Describe the physical, chemical, and biological processes necessary for wastewater treatment processes.
-Understand the water pollution control.
-Apply the operational steps in water and wastewater treatment processes.
Unit Processes I & II
Main topics included are hydrolysis, esterification, oxidation, nitration, sulfonation and sulfation reactions in chemical process industries. This module deals with the principles, properties and application of various types of reagents and prime factors influencing the design of nitrators, and also possible side reactions during sulphonation.
Learning Outcomes
Unit Processes I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the process technologies of various organic and inorganic process industries.
-Describe the principles of oxidation, esterification and hydrolysis reactions in chemical process industries.
-Know the properties of various types of oxidizing gents, esterifying agents and hydrolyzing agents in chemical process industries.
-Apply the technology in manufacture of various inorganic and organic chemicals.
Unit Processes II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the principles of nitration, sulfonation and sulfation reactions involved in chemical process industries.
-Understand various types of nitration agents, sulfonating and sulfating agents.
-Analyze the pathway of the derivatives through the reactions.
Unit Operations I & II
This module gives an overview of mass transfer, phase equilibria, distillation, extraction and absorption. It involves the study of the fundamental principles of diffusion phenomenon and mass transfer. This unit also provides the equipment, different methods of computation and thermodynamic conditions related to the necessary experimental design.
Learning Outcomes
Unit Operations I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand mass transfer and diffusion in gas, liquid and solid molecules.
-Derive the equations to relate the necessary experimental data and the unknown phase conditions, temperature and pressure.
-Understand the separation techniques.
-Solve the problems related to distillation in chemical process industry.
Unit Operations II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to :
-Compare and contrast the concept of liquid-liquid extraction vs. solid-liquid extraction.
-Derive the mathematic equation of extraction processes.
-Solve the problems using the properties and relationships of extraction processes.
-Understand the mechanism of absorption process.
-Derive the mathematic equations for absorption process.
Industrial Physical Chemistry II & III
This module focuses on basic principles, concepts and mechanisms of chemical engineering kinetics and reactor design. It also provides on study of multiple phase reactions and reaction limitations in continuous and batch type reactors.
Learning Outcomes
Industrial Physical Chemistry II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Study the rate of chemical reactions and factors affecting the rate of chemical reaction.
-Understand reaction mechanism of chemical reactions.
-Classify the order of reaction and molecularity of chemical reactions.
-Apply various experimental techniques to measure the rate of a chemical reaction, order of reaction, rate constant, molecularity and activation energy in chemical process industries.
Industrial Physical Chemistry III
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the fundamental principles and concepts related to chemical reaction engineering and chemical kinetics.
-Apply these concepts and principles in the analysis of reaction systems.
-Analyze batch and continuous reactor system, multiphase reactor systems and their effects on the reaction.
Petrochemicals
This module gives an overview of the current and future technologies for the oil and gas industry. It involves the study of petrochemicals digest and their derivatives.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the sources of petrochemicals, techniques, skills and modern tools necessary for the processing of petrochemicals, synthetic gas and detergents.
-Categorize the key products and derivatives of petrochemicals in petroleum based industries.
-Understand the production routes of petroleum based industries.
Plastic Technology
This module gives an overview of the current and future technologies for plastic industry. It involves the study of the fundamental principles of plastic moulding techniques, modern plastic and general properties for design considerations.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the types and characteristics of raw materials in plastics industries.
-Know the types of plastics, plasticizers, fillers, resins and polymers.
-Understand the manufacturing and polymerization processes, molding techniques and the development of plastics products.
-Know the techniques for the production of elec¬tronic equipments, microelectronic devices and other industrial application.
Fourth Year
Course Description
Process Engineering Economics I & II
This module aims to introduce plant design and economics analysis for chemical engineers. It involves the determination of optimum operating conditions in experimental design, cost estimation and industrial management. Moreover, the leadership and management skill can be taught in this module.
Learning Outcomes
Process Engineering Economics I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Analyze the optimum operating conditions for minimum cost of a process.
-Apply the concept of alternates based on the quantity or yields.
-Understand the cost estimation of an industry/ factory.
-Evaluate the economic feasibility of new processes and products.
Process engineering Economics II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the role of leadership and management of differences and conflicts.
-Understand complex ideas and tolerate ambiguity in managerial and organisational problem-solving.
-Understand the basic managerial decisions.
-Manipulate economic analysis for a selection of plant site.
Unit Processes III & IV
Mechanisms of hydrogenation, polymerization, alkylation and industrial polymerization practices can also be learnt in this module. Moreover, it can give the knowledge on the production and application of different resins, covering the alkylation and types of alkylation.
Learning Outcomes
Unit Processes III
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the principles and mechanism of hydrogenation and polymerization reactions involved in chemical process industries.
-Describe the importance of hydrogenation and polymerization catalysts.
-Analyze the techniques of hydrogenation in the production of various types of hydrogenated compounds.
-Apply the polymerization reactions in industrial processes.
Unit Processes IV
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the principles and mechanism of alkylation and polymerization reactions involved in chemical process industries.
-Know the types of alkylating agents in alkylation and catalysts of particular polymerization reactions.
-Apply the technical unit processes and principles of alkylation to produce alkyl aryl detergents.
-Understand industrial polymerization practices.
Unit Operations V & VI
This module gives an overview of filtration, crystallization, drying and their industrial applications. It also provides the empirical and fundamental tools in the design of the process and equipment.
Learning Outcomes
Unit Operations V
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand and apply the basic methods of crystallization.
-Evaluate efficiency and requirements of unit operations encountered in process engineering.
-Manipulate empirical and fundamental tools in the design of equipment and processes.
Unit Operations VI
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the basic concepts of drying and adsorption processes in each respective field.
-Know about the dryer types and their classification and operations.
-Study the mechanism of adsorption and types of adsorption, adsorbents and their uses.
-Apply the fundamental theory of adsorption of solid when contacting with fluid mixture and solve the problems encountered in chemical process industries.
Selected Topics in Industrial Chemistry I
This module includes the identification of industrial oil and fat products and also involves the description of their refining and production methods. Moreover, the student can learn the manufacturing processes and uses of soap and detergent, and nitrogen and nitrogen based products. As part of the module, the student can learn research methodology for contribution of research concepts, ideas, laboratory rules, academic writing format and style.
Learning Outcomes
Selected Topics in Industrial Chemistry I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand in the processing and analysis of fats and oils, soaps, detergents and fertilizer.
-Analyze the unit operations and processes involved in manufacturing.
-Understand the basic concept of research methodology, management process and laboratory housekeeping.
-Manipulate research systemically and effectively contribute to the community.
-Write an original/ good research/ project paper.
Industrial Inorganic Chemistry
This module aims to introduce the concepts and principles related to inorganic chemistry and nuclear chemistry. It provides limitations of composites materials used in chemical process industries, properties and uses of the nuclear fuel in nuclear power plants and fundamental concepts of corrosion and the related problems encountered in oil and gas industries.
Learning Outcomes
Industrial Inorganic Chemistry
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the main raw materials, production, properties and uses of composite materials
-Distinguish the types of matrices and reinforcement.
-Discuss the advantages and limitations of composites materials used in chemical process industries.
-Know the fundamental of radioactivity, radioactive decays and nuclear reaction.
-Identify the properties and uses of the nuclear fuel.
-Understand the nuclear reactor and nuclear power plants.
-Understand the fundamental concepts of corrosion and the related problems encountered in oil and gas industries.
-Apply the prevention and protection methods in the piping systems.
Chemical Process Industries I & II
This module can give an access to the factors influencing their manufacturing processes of inorganic acids, pulp and paper products, cosmetic products, and how to prevent the environmental effect related to the chemical industries.
Learning Outcomes
Chemical Process Industries I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the manufacture of the followings: chlorine and sodium hydroxide, sodium, sulphur, sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid, some inorganic chemicals, portland cement and glass.
-Identify the influencing factors for the manufacturing process of inorganic and organic products.
Chemical Process Industries II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the sources, conversion process and manufacture processes of pulp and paper products.
-Manipulate the conversion techniques from biomass into useful products.
-Understand the ingredients used in cosmetics and their functions.
-Describe the basic formulation of a cosmetic product.
-Manipulate the development of cosmetic product.

